Researchers explore biomimetic approach for making adhesives tougher
A team from Purdue University takes inspiration from sea creatures to produce stronger adhesives with weaker bonds.
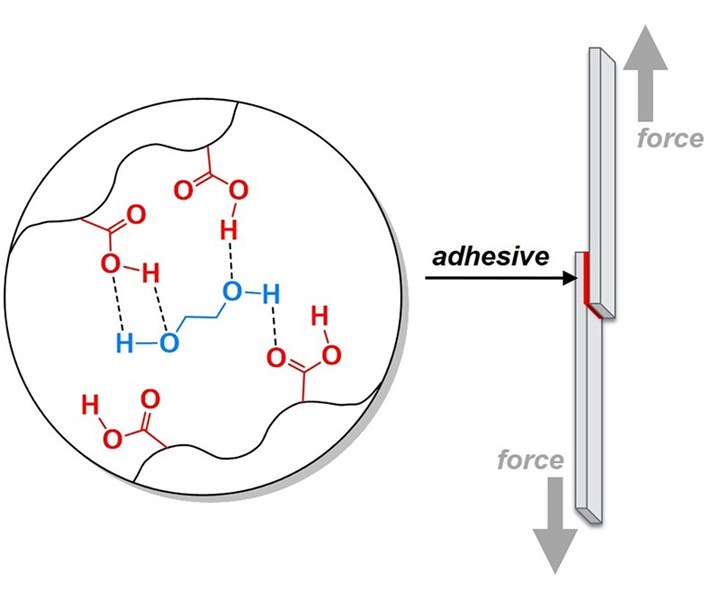
Purdue University researchers added bonds that are broken easily throughout the material to strengthen the adhesive. Source | Purdue University.
How do you make adhesives for electronics, vehicles and construction tougher? By making them weaker. That’s the proposed solution from a Purdue University (West Lafayette, Ind., U.S.) research team — well-known for its adhesive technology.
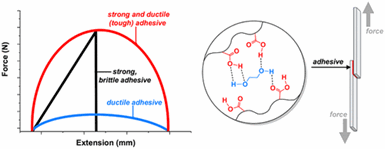
“We have been using inspiration from sea creatures to develop several new adhesives,” says Jonathan Wilker, a Purdue professor of chemistry and materials engineering, who helps lead the research team. The Purdue team added bonds that are broken easily throughout the material. When pressure or stress is applied to the glue, these sacrificial bonds are designed to absorb energy and break apart. Meanwhile, the rest of the larger adhesive system remains intact. The Purdue team’s work is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Managing how energy moves in adhesives
“The idea is somewhat similar to how a brick wall is made of bricks that are offset from each other,” says Wilker. “You stagger the bricks and cement so that a crack does not shoot right down through the cement lines. A crack hits the middle of a brick and the forces get spread out toward both sides, eventually decreasing to the point that the wall stays intact.”
Source | “Weak Bonds in a Biomimetic Adhesive …,” Journal of the American Chemical Society
“We added weak bonds within the adhesive so that mechanical forces and growing cracks lose energy by breaking these bonds instead of having the whole, larger material fracture. The idea is to manage how energy moves through the material. The overall adhesive system can become tougher and less likely to break apart when placed under mechanical stress.”
Wilker’s team tested this idea with several types of bonds. The ones that worked best were neither too weak nor too strong. He said that this technique for managing energy in adhesives might be a general phenomenon that could be applied to adhesives in industries ranging from consumer electronics to construction to manufacturing airplanes and automobiles.
Toxin-free adhesives

Oyster reef in the Baruch Marine Field Laboratory. Source | Jonathan Wilker/Purdue University
The team has hundreds of mussels and oysters growing in its laboratory for studying proteins used by the sea creatures attaching to rocks. After working to understand the nature of these natural adhesives, the researchers then generate several synthetic versions with different properties.
They have worked to patent several of their toxin-free adhesive systems with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization (OTC). The researchers are looking for partners to continue developing their technology. For more information on licensing and other opportunities, contact Joseph Kasper of OTC at jrkasper@prf.org.
Read the paper abstract below.
Related Content
Carbon Mobile carbon fiber powers handheld gaming platform
HyRECM technology effectively stabilizes carbon fiber’s electrical and antenna properties, enabling development of next-gen electronics, such as the Snapdragon G3x Gen 2.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Electronics (2025)
Electronic and smart device innovations achieved through the use of advanced materials ranging from thermoplastic composites to biomaterials emphasize high-volume production and sustainability.
Read MoreAviation-specific battery system uses advanced composites to address electric, hybrid flight
BOLDair’s composite enclosure, compression structures and thermal runaway management enables high-performance electric energy storage.
Read MoreGlobal research teams propose standards for structural power composites
Researchers have published a set of characterization and reporting protocols to accelerate the industrial adoption of SPCs, which combine structural strength with energy storage capabilities.
Read MoreRead Next
Thermoplastic composite materials and processing interactions
Selection of product material formats and their interactions with various process methods heavily influence a final TPC part’s properties and fabrication options.
Read MoreRobotic computed laminography brings X-ray CT resolution to large composite structures
Omni NDE collaborative robots, X-ray end effectors and Voxray’s reconstruction approach enables 5-micron inspection of aerospace parts without size constraints.
Read MoreCutting engine weight via thermoplastic composite guide vanes
Greene Tweed replaces metal stator vanes with its DLF material co-molded with a metal leading edge that meets performance, cost and high-rate production targets while cutting 4 kg per engine.
Read More