Additive Manufacturing/ 3D Printing Using Composites
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized composite production by enabling the layer-by-layer construction of intricate composite structures. In the realm of composites, additive manufacturing techniques allow for the creation of complex geometries with precise fiber orientations and resin distribution, optimizing material performance. This technology offers the flexibility to customize parts, reduce waste, and experiment with novel composite combinations. By depositing materials layer upon layer, additive manufacturing facilitates the production of lightweight, high-strength components tailored for specific applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, pushing the boundaries of what's achievable in composite design and fabrication.

ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALLAvoiding pitfalls in the design of LFAM composite components
Recoat temperature, part orientation and bead geometry are some key design variables to consider for a successful and reliable large-format additive manufacturing (LFAM) process.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
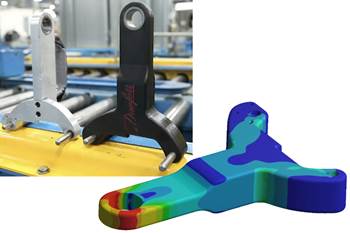
Read MoreHow to validate 3D-printed composite part performance
Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME) workflow simulates composite material performance to speed development, optimize performance and reduce costs for a redesigned 3D-printed CFRP bracket.
Read MoreContactless measurement of temperature, pressure in composites
Magnetic microwires enable contactless measurement of temperature and pressure during cure and in service.
WatchKnowledge Centers

The composites industry is increasingly recognizing the imperative of sustainability in its operations. As demand for lightweight and durable materials rises across various sectors, such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, there is a growing awareness of the environmental impact associated with traditional composite manufacturing processes.
LEARN MORELatest Additive Manufacturing News And Updates
Pantur integrates Reinforce3D CFIP to produce pilot, functional reinforced 3D printed parts
Through the Delta system installation, Pantur will integrate continuous fiber injection reinforcement into its additive manufacturing ecosystem, serving to increase the momentum of bringing CFIP to real industrial production.
Read MoreFlexCyle project targets TPC waste recovery, repurposing at same site
Led by the Brightland Materials Center, consortium members are developing a flexible process chain, demonstrated via battery casings and wind blades, to repurpose waste directly where it is generated.
Read MoreCaracol raises $40 million Series B to progress global scale-up
The international round marks a key milestone, consolidating Caracol’s leadership in Europe, the U.S. and the Middle East, supporting its exponential growth and fueling expansion into new markets.
Read MoreKorean researchers develop 3D printed CNT sensors for health monitoring, flexible electronics and smart textiles
CNT-based nanocomposites are optimized specifically for vat photopolymerization-type 3D printing, maintaining high stretchability and electrical conductivity.
Read MoreCaracol acquires Hans Weber’s additive manufacturing assets
Caracol will acquire Weber’s IP and additive technology with the goal of strengthening the LFAM technological roadmap for European customers and building up its presence in the DACH region.
Read MoreFIDAMC inaugurates CFA facility in Cádiz for composites innovation
FIDAMC’s Centro de Fabricación Avanzada (CFA), backed by over €18 million and 20 years of composites expertise, will drive multi-sector industrialization in 3D printing, robotics and sustainable materials.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
KraussMaffei makes LFAM both a product line and an internal benefit
Plastics processing equipment supplier now offers two LFAM machines to customers and to complement its own production uses, enabling a variety of polymer to fiber-filled application options.
Read More3D Fiber Tethering for rapid fabrication of continuous fiber composites
CarbonForm’s 3DFit technology combines robotic, continuous fiber 3D printing and winding to produce small, high-strength, complex parts — like drone frames — in as little as 10 minutes.
WatchCMH-17 updates composites data, will publish new Volume 7 on additive manufacturing
The Composite Materials Handbook-17 is publishing new data and industry best practices, helping to fill the aerospace industry’s growing knowledge transfer gap and support advanced materials and structures.
Read MoreCaracol North American headquarters can produce 100 systems per year
The Italian LFAM systems manufacturer has opened a new facility in Texas that will support application development, service and the production of its turnkey robot-enabled 3D polymer composite printers.
Read MoreOptimizing a CFRP landing leg demonstrator
MT Aerospace achieves design for manufacturing, integrating multiple elements into one-piece structure using AFP and 3D printed tooling to meet time and budget constraints.
WatchIn oil and gas, an additive manufacturing standard (API 20T) will aid adoption of composites
Polymer AM equipment maker Roboze sees how the oil and gas industry’s way forward with additive is like that of another high-stakes industry, aerospace, and also different in important aspects.
WatchFAQ: Additive Manufacturing
What is additive manufacturing in composites?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, in composites involves the layer-by-layer deposition of composite materials, such as continuous fibers or chopped fibers within a matrix, to create complex parts or structures.
What types of additive manufacturing methods are used for composites?
Various methods are employed, including Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), Continuous Fiber 3D Printing (CFF), Binder Jetting, Directed Energy Deposition (DED), and others that selectively deposit materials to build composite parts.
What composite materials can be used in additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing processes can work with a range of composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs), glass fiber composites, and even advanced materials like nanocomposites or hybrid composites.
What are the advantages of additive manufacturing in composites?
Benefits include the ability to create complex geometries, lightweight structures, reduced material waste, customization, rapid prototyping, and the integration of functional features within parts.
Are there limitations to additive manufacturing in composites?
Challenges include limitations in scaling for large-scale production, post-processing requirements, ensuring consistent mechanical properties, and the need for advancements in material options.