CompoTech participates in three new R&D projects for expanded use of composites
Multiyear programs explore composites in mechatronic systems, integrated fuel tanks for hydrogen and high-rigidity opto-mechanical systems.
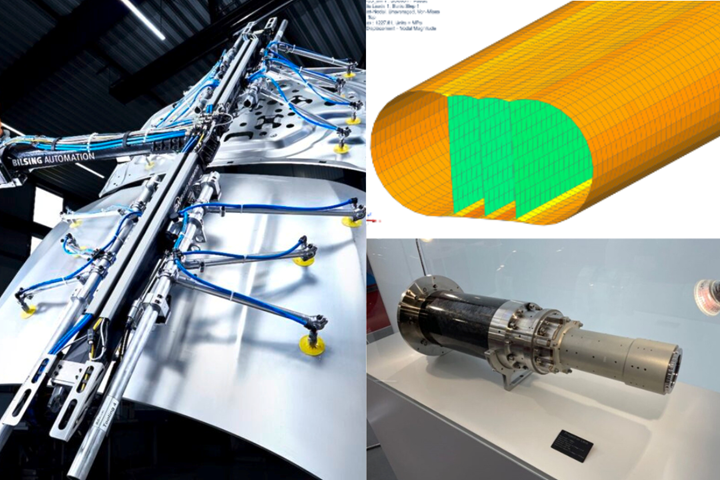
Bilsing Automation composite T-boom (left), pressure vessel design concept #2 (top right) and an optical device with a carbon fiber tube (bottom right). Photo Credit, all images: CompoTech
CompoTech (Sušice, Czech Republic) plays an active role in academic research and development (R&D). This year, three projects that the company is participating in have been awarded funding from the Technology Agency of Czech Republic. The research spans a variety of different sectors with associated research bodies and universities, and includes mechatronic systems, integrated fuel tanks for hydrogen and high-rigidity opto-mechanical systems. All projects run from January 2023 to December 2028.
Advanced design of opto-mechanical systems
Cooperation between Compo Tech Plus and Meopta – Optika (Přerov, Czech Republic) initially began with R&D activities introducing composite materials into opto-mechanical devices for the optical and semiconductor industry. The advantages and disadvantages of composites were tested, and several components were manufactures and successfully applied into a serial production and design chain in both companies.
To further enhance the knowledge needed for such semiconductor-related applications, CompoTech and Meopta – Optika have joined a research project initiated under the National Competence Centre. Other partners include Czech Technical University (Prague) and HiLase (Dolní Břežany, Czech Republic).
Specifically, the project is focused on the development of high-rigidity composite structural parts for opto-mechanical assemblies, like the one given in the following example. Replacement of heavy stainless steel or granite frames with lightweight composites could lead to mass reduction of structural frames. Using CompoTech’s technology, ultra-high modulus fibers are being applied into the design, leading to optimized structural stiffness and good damping behavior. Moreover, the low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the fibers reduces the frame’s deformation behaviors under thermal loading.
Throughout the project, technology development, together with simulation models and design approaches will be developed, manufactured and tested on large structural frames, using the abilities of all participants. One important area is to design the carbon fiber frames with surface protection, which works in semiconductor industry cleanrooms.
Composite integral fuel tank for pressurized hydrogen
Under this project, led by the National Competence Centre for Aeronautics and Space (NaCCAS), a pressurized tank using CompoTech’s advanced winding technology is targeting the development of a linerless Type V fuel tank.
The goal of the project is to produce a functional segment sample of a non-standard-shaped composite tank for gaseous fuels such as hydrogen for use in aviation. This tank will assume integration into the primary structure of the airframe of the Distar CZ a.s. (Ústí nad Orlicí, Czech Republic) Lambáda motor glider (or similar aircraft) and will carry partial loads from the aerodynamic and mass forces acting on the aircraft.
Energy-saving technologies and materials for sustainable development in mechatronic components
CompoTech Plus and the Department of Mechanics, Biomechanics and Mechatronics at Faculty of Mechanical Engineering of Czech Technical University in Prague are cooperating under the NCK Mestec research project to combine lightweight, high-rigidity composite structures with mechatronic systems. Project partners aim to enhance the mechanical properties of structural frames, their speed and positioning precision to further improve the productivity of automotive industry automation lines.
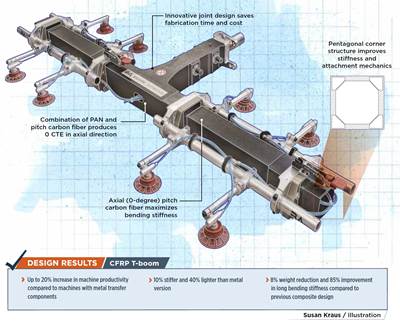
Composite frames and structural assemblies attached to robot-based manipulators are being analyzed with different mechatronic systems to ensure frame damping and deflection are improved in static and dynamic loading by the mechatronic and advanced control systems. R&D activities for 2023-2024 are focused on a composite T-boom frame, which is usually applied in automotive for fast part transportation. The standard lightweight frame fabricated from ultra-high modulus carbon fiber is being compared virtually using simulation models with different mechatronic approaches. In following years, the new designs will be manufactured and compared with the reference standard approaches.
CompoTech cites that it has been active in the area of industrial and automotive automation components for many years. Its carbon fiber frames have already been successfully integrated into production lines and other automation system worldwide, with a long-term cooperation with Bilsing Automation.
Related Content
Stadler H2 train achieves Guinness World Record title
The Flirt H2 now holds the world record for longest distance traveled by a hydrogen-powered passenger train without refuel or recharge, aided by Type IV composite tanks.
Read MoreComposite bipolar plates provide 81% improvement to hydrogen fuel cell power density
Ultra-thin CFRTP plates developed by Hycco achieve a 7.5 kilowatt/kilogram power density, high durability for fuel cells in long-flight drone and heavy-mobility applications.
Read MoreAirbus outlines next-gen single-aisle aircraft technology focuses, revised ZEROe project roadmap
Outlined technology bricks — including foldable wings, more efficient engines and propulsion and composite materials — could support a planned single-aisle next decade, plus Airbus’s renewed commitment of a commercially viable H2 aircraft.
Read MoreComposite pressure vessels enable future energy storage
Q&A between Hexagon Purus, Infinite Composites and Hyosung USA delves into the future of H2 storage, including scalability and production goals, materials and application trends and other dynamics.
Read MoreRead Next
Composite T-boom accelerates industrial automation
A manufacturing method that integrates filament winding with axil winding of 0-degree fibers opens new design options in industrial automated equipment.
Read MoreComposite molding compound replaces Invar for lightweight small satellite structures
Patz Materials and Technologies and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory developed a new monolithic optics housing with 80% less weight, near-zero CTE and the high-volume manufacturing required for commercial space.
Read MorePolestar 5 takes aesthetics and circularity approach to biocomposite seatback design
The 2026 Polestar 5 expands the company’s use of sustainable materials design in the interior, including flax fiber/thermoplastic seatbacks that save 7 kilograms of weight and reduce overall plastics use.
Read More