JEC COMPOSITES 2009 Product Showcase
Despite the doleful state of the global economy, the turnout in Paris — exhibitors and visitors — proved surprisingly strong.
Share
Read Next
The consensus on the show floor at the 2009 edition of the JEC Composites Show was that although attendance this year did not equal 2008 levels, the turnout was greater than expected. Postshow statistics released by show organizers tended to support that contention. By JEC’s count, 1,065 exhibitors (75 percent from outside France) and 25,500 visitors from France (35 percent) and 95 other countries. Some observers credited the attendance levels at the show, held March 24-26 at the Paris Expo in Porte de Versailles, Paris, France, to the fact that JEC highlighted neighboring Germany as its featured guest country and selected an “Automation” theme, which attracted new European exhibitors that offer automated solutions. According to JEC, visitor traffic was actually up significantly this year in four market sectors: wind energy, 35 percent; aerospace, 28 percent; building and construction, 18 percent; and — very surprising, given plummeting new car sales — automotive, 16 percent. JEC says the unexpected statistics owe much to an increase in traffic from composite component end-users.
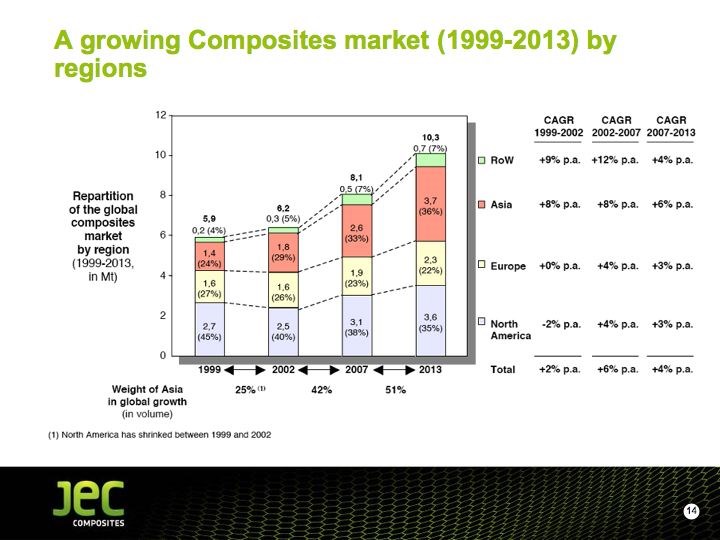
At a show press conference, JEC Group president/CEO Frédérique Mutel added an upbeat note to the gathering with a presentation of JEC’s latest composite market study figures, which puts the worldwide market value of the composites industry at €62 billion ($82.4 billion USD) with a total volume of 8.6 million tonnes (18.9 billion lb). Despite the recessionary climate, her take is that the compound annual growth rate through 2013 will be at 4 percent, with the largest growth occurring in Asia (see photo, p. XX). The growth rate should be faster than the gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate, says JEC, with building and construction and wind energy the fastest-growing market segments.
In other show-related news, SAMPE Europe, JEC and the organizers of the AUTOMATICA conference signed a joint agreement to collaborate at the next AUTOMATICA gathering in 2010. A dedicated “Composites Pavilion” organized by JEC Composites and a two-day trade conference organized by SAMPE Europe will help advance automation methods in the composites industry, say the three groups. The conference portion of the collaboration, to be entitled "Advanced Composites for Automatization,” is being organized by Dr. Klaus Drechsler of the Technical University of Munich.
On the Paris show floor, HPC staffers found the following notable news and developments.
Tooling & out-of-autoclave prepregs
Advanced Composites Group Ltd.’s (ACG, Heanor, Derbyshire, U.K.) large and busy stand showcased several of the group’s accomplishments, including commercialization of trademarked DForm deformable composite system (DCS) prepreg material for tooling and out-of-autoclave prepregs for a variety of industries. The company announced a three-year supply agreement with Southern Spars (Auckland, New Zealand) under which ACG will supply its MTM prepreg for Southern’s carbon fiber spars and rigging. Also announced was the company’s attainment of ISO TS 16949 market accreditation from Lloyd’s Register for automotive industry applications.
ATL system for thermoplastics
In its first stint as a JEC show exhibitor, Advanced Fibre Placement Technology BV (AFPT, Sprang-Capelle, The Netherlands and Dörth, Germany) showed its automated tape laying (ATL) system, which features a single thermoplastic tape-laying head mounted on a robotic arm. The head uses a laser to heat the tape prior to consolidation rather than a hot gas torch or other conventional technology. The company offers several tape placement systems for industrial applications or R&D activities. ATL-compatible software tools are available to AFPT through its partnership with CGTech (Irvine, Calif.).
[hpc_jul_09_jec_airtech.jpg]
Self-releasing, multilayer bagging film
Airtech International (Huntington Beach, Calif.) attracted crowds at its stand with frequent demonstrations of vacuum infusion, using the company’s line of bagging material and components. The company emphasized its Dahlar Release Bag 520, a self-releasing, multilayer vacuum-bagging film designed for direct contact with prepreg when fabricating hollow parts. The film reportedly maintains vacuum at temperatures as high as 220°C/428°F and can be used with lay-flat tubing and gusset-folded tubing for internal bagging of hollow parts. Also featured was the ultrawide (12m/39.4 ft) Securlon L500 bagging film and Airseal 1 and Airseal 2 bag sealant tapes. The company also announced that its online catalog (www.airtech.lu) is now available in English, French, German, Italian, Spanish and Russian.
New machinery expands 3-D weaving capability
BITEAM AB (Stockholm, Sweden) shared a stand with Oxeon AB (Borås, Sweden), its innovation partner. BITEAM introduced its industrial 3-D weaving machine, jointly developed with the Department of Lightweight Structures, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH, Stockholm, Sweden), under the “MOJO” European 6th Framework Project. The 3-D weaving machine, based on technology invented by company cofounder Dr. Nandan Khokar, can produce complex profiles including tubular, flanged cruciform and other shapes in any type of fiber or fiber combinations. A sample of a double-flanged box beam produced by the machine was on display, together with Oxeon’s TeXtreme and TeXero spread tow woven textiles used in many applications, including Formula 1 racing.
Testing site Nadcap-certified
Materials testing and engineering group Bodycote Testing Ltd. (Salford, U.K.) announced that it’s European Technology Centre in Linköping, Sweden, has been approved by Nadcap (Warrendale, Pa.) for the testing of composite materials for the aerospace industry. The lab is reportedly one of the first in the world to receive approval for this type of testing. Nadcap is a cooperative of major companies supplying the aerospace industry and was designed to provide a cost-effective consensus approach to special processes and products.
Hot-melt adhesives with high heat resistance
Collano Adhesives (Sempach-Station, Switzerland) demonstrated its range of specialty adhesives for a range of demanding applications, including noise abatement and vibration damping. The company offers a broad range of hot-melt adhesive films that exhibit high heat resistance. Designed for the transport industry, for use in trucks and other ground vehicles, aircraft, railcars, vessels and interior fittings, the products can be applied with precision, using automated techniques, and quickly processed. Multilayer films also are available. The company’s reactive hybrid adhesives, based on silanes and epoxy resins, address requirements in load-bearing vehicle, ship and container fabrication processes.
Crush-simulation software for composites
Dassault Systèmes (Paris, France and Providence, R.I.) emphasized its recently released CZone for Abaqus, from the DS SIMULIA brand. A new add-on product for Abaqus finite element analysis (FEA) software, the program simulates crushing of composite materials, enabling engineers to accelerate the design and evaluation of energy-absorbing composite components and assemblies. Based on technology from Engenuity Ltd. (West Sussex, U.K.), the new product provides the ability to study the crashworthiness of composite structures in automobiles, helicopters, aircraft, railcars and other vehicles to protect occupants and cargo from shock or injury during severe impact.
Structural health monitoring
Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft (Darmstadt, Germany) focused its presence at the show on structural health monitoring systems in aircraft wings. In its stand it had an aircraft wing with 42 sensors integrated in or applied to the structure to monitor loads, impacts and damage. By processing and interpreting all of the sensors’ signals, Fraunfofer researchers intend to correlate data with experimental tests, thus more accurately assessing the structes condition and health.
Prepregs for the automotive market
Hexcel (Dublin, Calif. and Duxford, U.K.) touted materials tailored for the automotive industry: HexPly M49 prepreg for car body parts and interiors; and HexPly XF3, a surfacing film that reportedly provides a ready-to-paint surface finish with minimum preparation and is compatible with most epoxy prepregs and adaptable to a wide range of cure cycles, from 100°C to 140°C (212°F to 284°F).
On display in the stand was a bonnet (hood) for the Lamborghini Gallardo, manufactured by ACE GmbH (Immenstad, Germany) using resin transfer molding with HexForce NC2 multiaxial carbon fabric, said to permit full resin infusion and provide a very smooth surface that reduces the print-through effect of the carbon. The Gallardo gear selector is manufactured with HexMC carbon fiber/epoxy that facilitates layup of parts with complex shapes.
Also of interest to automotive customers is the HexForce PrimeTex range of fabrics that have been processed for a smooth, closed weave and uniform cosmetic appearance. The fiber tows are spread via patented processes in both the warp and weft for unique aesthetic appeal. Trademarked PrimeTex fabrics are being used by automaker BMW on the inner and outer skins of the carbon/epoxy roof of the current M3 and M6 models.
Resins for fuel cells & aircraft interiors
Huntsman Advanced Materials (The Woodlands, Texas) received a JEC Innovation award in the “Raw Materials” category for two new resin systems based on benzoxazine and bismaleimide chemistries. The new resins allowed Huntsman’s award partners GrafTech International (Parma, Ohio) and Ballard Power Systems (Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada) to produce next-generation bipolar plates for fuel cell applications. The system is based on a phenolic-like backbone and operates at continuous temperature of 248°F/120°C. For stationary and back-up power applications, Huntsman introduced a flame-resistant bismaleimide resin, designed for use in fuel cells that operate at temperatures of up to 356°F/180°C in concentrated phosphoric acid. This material can be used in conventional prepregging processes. Fuel cell materials should be commercially available later by early 2010.
Ultrasonic camera for real-time NDI
Imperium Inc. (Silver Spring, Md.), a provider of ultrasonic camera solutions for nondestructive inspection (NDI), reported that Hexcel Corp. (Stamford, Conn.) has selected Imperium's Acoustocam I-500 for use by its Dublin, Calif., research lab to support application engineering efforts related to composite material inspection and evaluation of its HexMC molding material and other composite materials. Alfonso Lopez, application engineer for Hexcel, said, "Imperium's Acoustocam I-500 provides a terrific solution for non-NDI certified engineers to easily and effectively evaluate our composite materials in real time. Our investigation of other NDI equipment indicates that they do not offer such unique value."
Autoclave with external gas-fired furnace
Italmatic (Lucca, Italy) exhibited its line of autoclaves for composites curing. Company manager Roberto Frediani described a recent, highly efficient installation for Stork Fokker AESP (Papendrecht, The Netherlands) that uses an external gas furnace to heat the process air, rather than a direct combustion, electric heating source within the vessel itself. Hot air is transferred from the furnace via a closed loop to the pressure vessel through a heat exchanger; a ventilator inside distributes the hot air throughout the vessel to evenly heat the parts. The hot exhaust from the vessel stays in the closed loop to preheat incoming air and reduce the amount of heat energy required by the furnace. The system is designed for high thermal efficiency (82 percent), low-temperature exhaust, low NOX and CO2 emissions and minimum maintenance. The concept reportedly saves Stork Fokker significant energy costs while providing enough heating capacity for curing high-temperature thermoplastic parts. The system will be protected by an international patent.
Nesting & NC-code software for cutting systems
JETCAM International (Monaco) announced a new suite of software applications at JEC, including JETCAM Expert, which provides a nesting engine and NC-code output for cutting systems used on composites. As part of this rollout, the company challenged visitors to provide CAD files of existing parts along with a DXF file of their of best attempt to nest those parts. JETCAM then provided a comparison, using its High Performance Nesting engine, which reportedly can provide material savings of 5 to 15 percent. The company also launched its Material Life Management (MLM) software, which stores and then provides users with real-time data about available materials, including material stock levels, material left on a roll, material location, expiration date, how long each material has been out of the freezer, and other data.
Materials for aircraft interior and spacecraft repair
High-Performance epoxy specialist Magnolia Plastics Inc. (Chamblee, Ga.) came to Paris to publicize two materials for use in aircraft interiors. Magnolia 85-3 A/B is a lightweight, rapid-curing, epoxy syntactic designed for edge fill in honeycomb panels. It sets in 15 minutes, cures in seven days and has a pot life of 3 minutes. Magnolia 121-146 A/B is a lightweight epoxy potting and filling adhesive dispensed from side-by-side cartridges. It sets in 15 to 30 minutes and fully cures in seven days. Also, Greg Bunn, Magnolia’s director of research and development, reported that the company has been working with Scaled Composites (Mojave, Calif.) to develop customized composite repair systems for SpaceShipTwo and WhiteKnightTwo, the suborbital spacecraft and mothership/launch platform that will soon transport paying customers to the edge of space for space tourism company Virgin Galactic (London, U.K.). www.magnoliaplastics.com
AFP/ATL machine code software
Relatively new to the composites industry and the show was MIKROSAM AD (Prilep, Macedonia), which introduced MikroPlace, software designed to allow automated fiber placement (AFP) and automated tape laying (ATL) machinery users to produce NC code from CAD data. It allows the user to draw or import the part’s tool, create ply laminates, export the design for analysis to a finite element analysis (FEA) package, analyze and fix production problems and do custom post-processing modifications of the final layup. The software is machine independent and can import design data from CATIA, Pro/Engineer, Autodestk Inventor, SolidWorks and others.
[use image from CT JUN 09 on Web]
Fiber-reinforced polyurethane foam core
Milliken & Co. (Spartanburg, S.C.) attracted interest from show visitors with its NexCore fiber-reinforced polyurethane foam core product for composite sandwich constructions. The product, now commercially available, is made in a continuous process, with triangular closed-cell foam elements encased in noncrimp E-glass fabric. The “truss” design, when infused as part of a sandwich structure, gives the core high toughness and durability and equal stiffness at a lower weight than comparable cores, reports the company.
Sizing agent and nano-enhanced prepreg
Nanocyl SA (Sanbreville, Belgium) introduced two new products, SiziCyl and PregCyl. SiziCyl is a patented sizing agent that features carbon nanotubes and is designed for use with infusion and resin transfer molding (RTM) processes. PregCyl is a range of prepreg materials that also uses carbon nanotubes. It can be applied to unidirectional material or fabrics.
Aerostructures merger
The JEC show marked the debut of Premium AEROTEC GmbH, which began operations on Jan. 1 and comprises the former EADS Deutschland GmbH plant in Augsburg, Germany and the Airbus Deutschland GmbH plants in Nordenham and Varel, also in Germany. Each facility has been heavily involved in development of composite aerostructures for several years, including the carbon fiber composite rear pressure bulkhead for Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner and the cargo door for the Airbus A400M military transport aircraft. The Nordenham facility will produce some fuselage sections for the Airbus A350 XWB, as well as assemble fuselage sections for the plane.
Water-based multipart mold release
REXCO Mold Care Products’ (Conyers, Ga.) Partall POWER liquid mold release made its debut. The water-based, nonhazardous, silicone-free, semipermanent external mold release agent is designed to form a high-gloss finish on molded parts. Designed for use on most mold substrates (e.g., composite, aluminum and steel), the product reportedly provides multiple releases, yet offers ease of application with superior wet polishing and minimal fouling of tooling during processing. Recommended for use with most thermoset resins, it can be wiped on or spray applied over a sealed mold to form a smooth, durable, glossy film with excellent adhesion to the interfacial coating. Odorless, nonhazardous, and nonflammable, the product contains no hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) or volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
[hpc_july_09_jec_roctool.JPG]
Inductively heated molding system demonstrated
RocTool (Le Bourget du Lac, France and Atlanta, Ga.) periodically demonstrated its high-speed thermoplastic composite molding process, producing composite laptop computer covers on the company’s Cage System. The Cage System features an inductive heating system that heats only the thickness of the mold surface, providing for rapid ramp to molding temperature and fast cooldown cycling. A blank of material can be elevated from 50°C/122°F to 250°C/482°F in 70 seconds before forming, enabling users to achieve part production cycles of just over two minutes. Material for the covers was provided by Roctool partner Performance Materials Corp. (PMC, Camarillo, Calif.) and consists of unidirectional carbon fiber (12K and 24K) in a PET resin matrix. The covers, designed to compete with magnesium versions, have wall thickness of only 0.8 mm/0.03 inch, offer competitive cost and stiffness and emerge from the mold ready to paint. PMC is a licensee of the Roctool Cage System process and is working with laptop manufacturers on supply agreements.
24K carbon fiber for industrial applications
Toho Tenax Europe GmbH (Wuppertal, Germany) introduced its new trademarked Tenax-E IMS65 24K fiber, commercially produced on one of the newest production lines in Germany. Also showcased was Tenax-E UTS55 24K, an ultrahigh-tenacity fiber still under development that offers enhanced tensile properties and is targeted for high performance industrial applications, such as offshore oil piping and pressure vessels as well as for aerospace use. The fiber will be produced on a new line in Germany, currently under construction, which the company says will be finalized in August this year. Also available is a short fiber type specifically designed for high temperature resin systems. Tenax-A HT C723 (6 mm/0.24 inch) has thermal stability approaching 500°C/932°F, making it applicable for reinforcing high-temperature thermoplastics from polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) to polyetheretherketone (PEEK).
Laser templating systems sale announced
Virtek Vision International Inc. (Waterloo, Ontario, Canada), a subsidiary of Gerber Technology (Tolland, Conn.), signed an agreement at the show with Stork Fokker AESP (Hoogeveen, The Netherlands) for the latter’s purchase of laser templating systems over the course of the next five years. In the published announcement, Virtek’s VP for imaging and templating, Peter Richter, commented, “We are extremely pleased at having an important and prestigious aerospace manufacturer such as Stork Fokker place their long term trust in our products.”
Composites engineering software
New from VISTAGY Inc. (Waltham, Mass.) is AeroSuite, a software solution that enables aircraft manufacturers to more effectively manage the evolving product development process and deliver optimized parts and assemblies in less time at lower cost. AeroSuite consists of FiberSIM and SyncroFIT software for assembly development and the Quality Planning Environment. The company also showed the latest version of its suite of composites engineering software, FiberSIM 2009, which enables users to more easily define composite parts, provides improved functionality for resolving manufacturing issues and enhances the link between analysis and design. The new release reportedly simplifies composite part design with the addition of the global stagger profile, partial boundary editor and design checker as well as enhancements to zone-based design and core definition tools. Other features include improved tools for resolving manufacturability issues in FiberSIM 2009 with significant enhancements to the optional Automated Deposition Design (ADD) module. FiberSIM 2009 also features expanded integration of analysis and design with enhanced definition and interoperability between CAE and CAD for composite design.
Reconfigurable flatbed cutter/router
Zünd Systemtechnik AG (Altstätten, Switzerland) highlighted its award-winning new G3 digital table cutting/routing system, which is highly configurable for many materials thanks to its modular tool design. The G3 is available in nine different sizes, says the company, and can be easily customized to meet customer requirements. Its readily changed modular tool heads include rotary or oscillating knife blades or routers. Together with its cutters, Zünd also offers GTK “Autonester” nesting software for efficient ply cutting.
Related Content
Hexcel introduces mid-temp Flex-Core HRH-302 honeycomb core
Bismaleimide (BMI) option to serve complex curvatures and thermal management needs of military, commercial and UAM aircraft.
Read MoreSyensqo composites demonstrate titanium replacement on Boeing MQ-25 Stingray
Validation of integrating Cycom 5250-4HT prepreg into the UAV’s exhaust nozzle structure underpins the material system’s use in other high-temperature aerospace applications.
Read MoreLow-temp demold BMI prepreg enables low-cost master molds
CAMX 2025: Kaneka Aerospace 250°F BMI prepreg tooling, developed in collaboration with Janicki Industries, elevates composite tooling capabilities.
Read MoreKaneka, Janicki reveal study results for TP2230 BMI tooling prepreg
Lowering cure temperatures without compromising durability, Kaneka Aerospace BMI prepreg TP2230 offers aerospace manufacturers a pathway to reduce tooling costs and lead times while maintaining high-temperature capability.
Read MoreRead Next
Sentherm conductive polymers match aluminum thermal performance, cut weight
Tailored filler networks, anisotropic material design and manufacturing process control achieve hybrid polymers for EVs, batteries and other automotive-related electronics with 95% of aluminum’s thermal performance and 25-45% reduced component weight.
Read MorePolestar 5 takes aesthetics and circularity approach to biocomposite seatback design
The 2026 Polestar 5 expands the company’s use of sustainable materials design in the interior, including flax fiber/thermoplastic seatbacks that save 7 kilograms of weight and reduce overall plastics use.
Read MorePost Cure: CFRP mainframe, modern manufacturing techniques pioneer next-generation rigid airships
Advanced composites enable the revival of rigid airships in LTA Research's 400-foot-long Pathfinder 1.
Read More