AMRC and Prodrive partner to advance manufacturing of recyclable composite components
The companies have been collaborating on Prodrive’s P2T process, which is used for manufacturing recyclable composite components that can satisfy end-of-life requirements without any compromise in the performance of the original parts.
Prodrive Composites Ltd. (Milton Keynes, UK), is working with lightweighting and materials researchers at the University of Sheffield Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC, Sheffield, UK) to advance its processes for manufacturing recyclable composite components.
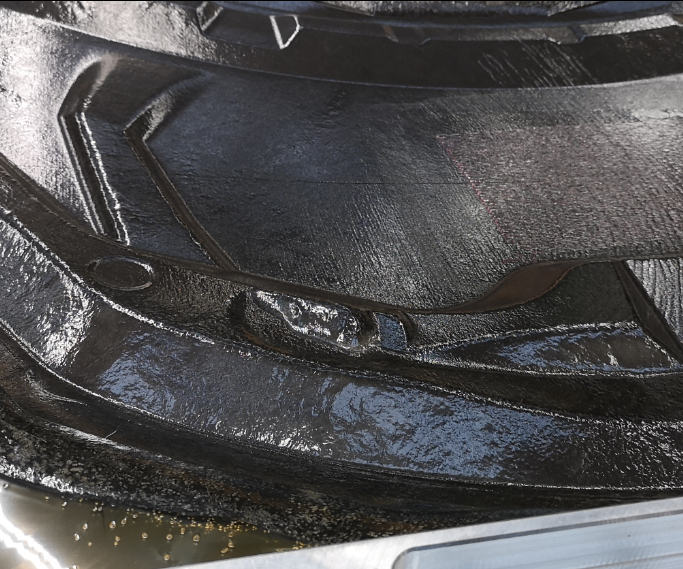
Prodrive Composites develops engineering solutions for automotive, aerospace and marine industries, and also designs and manufactures advanced lightweight composites for a wide range of applications across automotive, motorsport, aerospace, marine, defence and other specialist sectors. The company has been collaborating with the AMRC on its P2T (Primary To Tertiary) process, which is used for manufacturing recyclable composite components that can satisfy end-of-life requirements (specified in Directive 2000/53/EC) without any compromise in the performance of the original parts. The company claims the approach simplifies recycling and endows a composite material with the potential to fulfil three or more useful lifetimes.
Hannah Tew, partnership lead at the AMRC Composite Centre, says her team has been working with Prodrive Composites to further advance its recyclable composite process closer to full production. This has primarily focused on allowing for automation; making it possible to achieve medium to high volumes at substantially lower costs; looking at the recyclable nature of the materials used and increasing the technology’s attraction to other industries.
“The results from our initial press trials look promising and we’re very much looking forward to supporting Prodrive in automating the process going forward,” says Tew
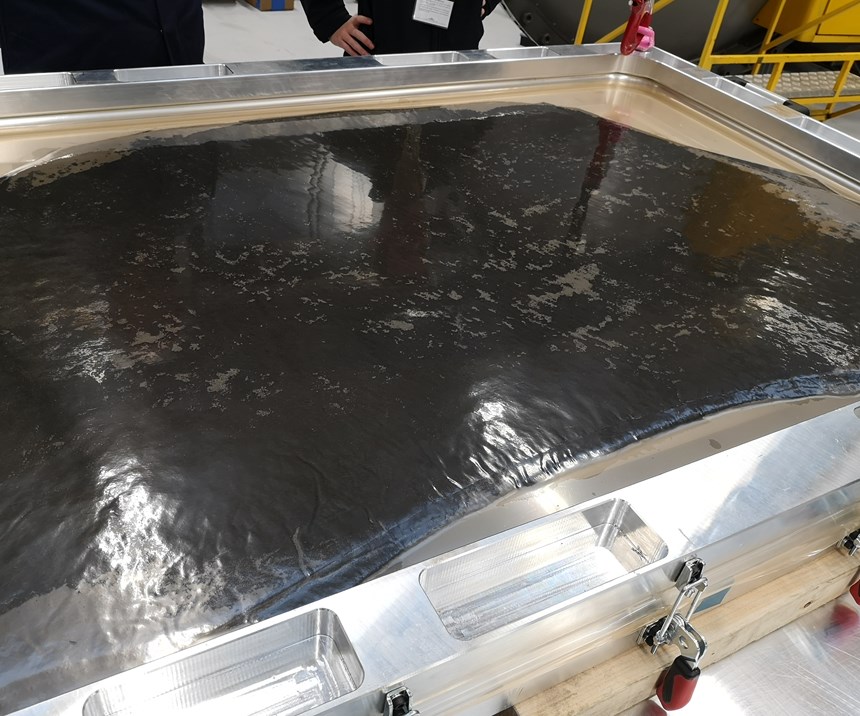
According to Prodrive, as P2T composites do not require heat or pressure during manufacture, there is no need for an autoclave – thus reducing costs and enabling the scaling up of production without major investment. The process uses a reactive thermoplastic resin instead of a thermosetting type; a plastic monomer is reacted with a catalyst in the presence of the fibers to produce a cured laminate.
Prodrive believes they are the first to develop this technique with recycled fibers, which emerged through a development program with an automotive OEM customer who required a high-performance structural material with lower environmental impact than conventional composites.
John McQuilliam, chief engineer at Prodrive Composites says:
“End-of-life recycling is one of the biggest debates in the composites world today. The issue affects automotive manufacturers and wider industries too, such as marine, where old fiberglass boats are often broken up and sent to landfill. The main barrier to recycling has been the type of resin used; thermosetting resins predominate but these cannot be readily recycled.
“We have been working with the AMRC and a series of large trial panels have been produced using an innovative process which can readily be automated. These trials have demonstrated that recyclable composite panels can be produced at a rate and cost to suit many industries.
“The unique feature of the P2T process is the reduced tooling cost and lead time compared to existing metallic or composite solutions.”
Prodrive Composites says that the advantages of composites produced by the P2T process is that they can be recycled multiple times. The highest mechanical properties are obtained during first use of the virgin fibers, enabling highly-loaded structural items to be manufactured. At the part’s end-of-life, the fibers and potentially the resin can be recycled, supplying much of the raw material for a secondary part, such as a body panel. When the secondary part reaches the end of its life, being thermoplastic, it too can be chopped and remolded into new parts with properties suitable for 3D solid components. This tertiary part can itself be recycled several times into lower grade parts.
The ongoing research between the AMRC and Prodrive Composites is set to expand over the coming year.
Related Content
Materials & Processes: Composites fibers and resins
Compared to legacy materials like steel, aluminum, iron and titanium, composites are still coming of age, and only just now are being better understood by design and manufacturing engineers. However, composites’ physical properties — combined with unbeatable light weight — make them undeniably attractive.
Read MoreTU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.
Read MorePlant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MorePEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More
.png;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)