AFRL camber morphing wing takes flight
Smooth composite skin enables active re-contour of up to 6% and fuel savings of 10%.
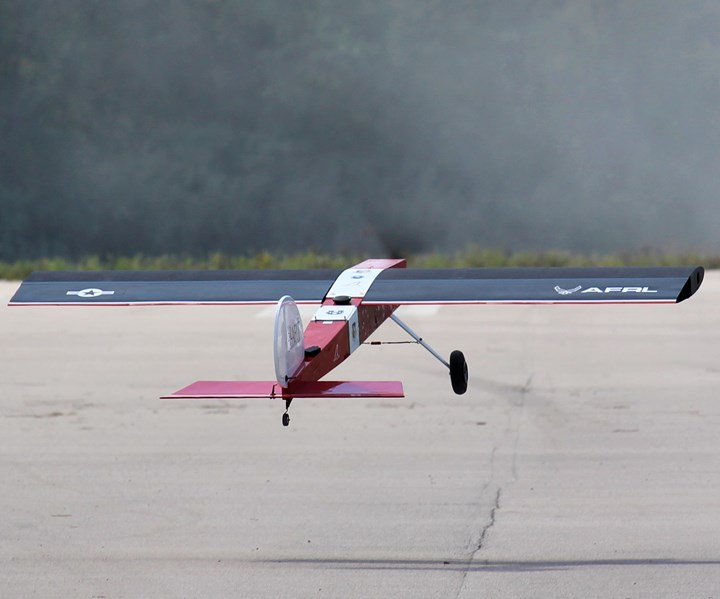

The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, U.S.) recently completed the successful flight demonstration of a game-changing camber morphing wing technology that could significantly increase aircraft range and performance.
The AFRL-developed Variable Camber Compliant Wing (VCCW) is capable of changing shape to improve aerodynamic performance and morph itself to various flight conditions and missions. Wing camber, or the shape of a wing surface, is a fundamental element of aerodynamic flight. Conventional wings with discrete hinged control surfaces have greater drag, whereas wings with a smooth camber are efficient and maneuverable. The ability to morph the wing according to aerodynamic conditions would give an aircraft increased lift when needed without a weight penalty — typically at takeoff and landing — and greater fuel-efficiency and maneuverability when in flight.
This flight experiment demonstrated the second iteration of the VCCW, a smaller, more compact version than the first, which was used primarily in wind tunnel experiments. This eight-foot wing was designed to be flown on a commercial-off-the-shelf remotely controlled aircraft, simulating an unmanned air vehicle. During the series of flights, held in September and October 2019, the wing was flown at low speeds, completing a number of maneuvers and demonstrating active shape control for optimized drag reduction and increased agility.
Single-piece, composite skin
The VCCW features smooth and continuous skin construction, which not only reduces noise by eliminating sharp surfaces and gaps, but improves aerodynamic performance as well. According to Dr. James Joo, AFRL Advanced Structural Concepts team lead and VCCW program manager, the improved aerodynamics translates into potentially significant fuel savings.
“Early estimates show VCCW technology saving aircraft fuel consumption by 10 percent,” said Joo. “This was one of our main goals, and it fits the Air Force’s efforts to reduce overall energy costs.”
According to a Dec 2019 article in TechBriefs.com:
“The wing can actively re-contour the airfoil camber up to 6% and the entire skin is seamless, continuous, and made of a single-piece, non-stretchable composite skin. Smooth conformal shape of the wing is attained by distributed elastic deformation from the underlying compliant mechanism and 3D shape change is also capable through variation of camber along the spanwise direction using a distributed actuation system along the span. Single actuation control for both leading and trailing edge deflection is another very unique aspect of VCCW compared to previous technologies. It was fabricated using advanced manufacturing technology enabling a solution that is lightweight, low power, and low cost.”
Advancing flexible wing technology
Jared Neely, AFRL research engineer and designer of the morphing wing, called this demonstration an important step in advancing flexible wing technology for warfighter use.
“The success of this demonstration has given us confidence that this technology can be leveraged to higher-class vehicles, to take advantage of the many benefits this technology can truly offer.”
Joo added that although other research organizations have explored the morphing camber concept, AFRL’s version is unique because it is a true flexible wing without any discrete control surfaces to assist in takeoff and landing. This seamless surface can increase overall range, making it ideal for a variety of long-range platforms. He says the team will continue to refine the concept and look into additional ways it can benefit existing aircraft.
“We are excited about the success of this demonstration,” said Joo. “We are continuing to explore the opportunities that this technology can offer for future Air Force aircraft development.”
Related Content
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreA new era for ceramic matrix composites
CMC is expanding, with new fiber production in Europe, faster processes and higher temperature materials enabling applications for industry, hypersonics and New Space.
Read MorePlant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreRead Next
CW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read More