CompositesWorld News for Jan. 17, 2020
Read news from AIMPLAS, Cevotec, and Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering (SAMPE)
Employment Opportunity: Senior Applications Engineer, Materia
Materia is seeking a Senior Applications Engineer for advanced composites applications.

Materia (Pasadena, Calif., U.S.) is seeking a Senior Applications Engineer to lead the engineering, processing project support and technical project management required for new customers to adopt Materia Proxima resins in advanced composite applications.
Essential Duties and Responsibilities:
- Serve as the engineering expert that supports new customers and development projects for advanced composite applications in major industries using pultrusion, filament winding, and HP-RTM/C-RTM processes.
- Develop process and manufacturing recommendations that enable customer adoption of Materia products.
- Collaborate closely with customer engineering teams to facilitate successful technology transfer and process scaleup.
- Coordinate and execute product trials and demonstrations at customer facilities.
- Work closely with colleagues to make test samples and provide technical feedback needed for developing new or improved resin processes and/or formulations.
- Maintain careful records, produce reports and other documents to meet technology dissemination, patent protection, and/or quality control needs.
- Work with colleagues to manage and maintain facility organization and safety.
Qualifications and Experience:
Education
- B.S. in engineering, material science or similar. Consideration will also be given to qualified individuals with a Certified Composites Technician Degree (CCT).
Experience
- 7+ years of relevant technical experience.
- Thorough understanding and experience with pultrusion processes and equipment for liquid thermoset resins is preferred; experience with HP-RTM, C-RTM and filament winding is a plus.
- Prior experience with direct customer interactions in a technical role
- Demonstrated technical problem-solving ability.
- Significant hands on experience and technical background related to working in laboratories and/or manufacturing environments.
- Strong oral and written communication skills.
- Good project and time management skills.
- Travel requirement: 25-50% expected (domestic and international).
- Location: Pasadena, Calif., U.S.
To submit an application, visit https://materiainc.applicantpro.com.
AIMPLAS develops flame-resistant resins for railway lightweighting project
As part of the European MAT4RAIL project, AIMPLAS developed flame-resistant hybrid resin formulations for composite structural components.

Source | AIMPLAS
The recently completed European MAT4RAIL project aimed to develop new materials and components for the “railway of the future,” and included efforts to reduce vehicle weight by replacing metal structural components with lightweight composites, as well as increasing vehicle capacity and passenger comfort through the use of smart modular design.
As part of this project, AIMPLAS (Valencia, Spain) reports that it has developed hybrid resin formulations with improved resistance to flame propagation to be applied to fiber-reinforced polymers, for use in structural components for railway vehicles. The company reports that results are promising and the new formulations are expected to be of use in other sectors such as construction, the automotive industry and aeronautics.
In addition, according to AIMPLAS, collaborative work was done to improve specific regulations on calculating fatigue requirements for trams, and involved efforts to standardize the design and calculation of trams by means of sensor monitoring, as well as evaluating and improving joins between metal and composite materials.

Source | AIMPLAS
The project also involved modifying the design of cabins and seats by incorporating new technologies and communication systems. The goal was to increase safety, detect the presence of extraneous objects on the tracks and improve vehicle intercommunication. Modular carriages were also developed to enable a range of configurations. A new seating design was developed to accommodate more passengers with greater comfort while offering more seating arrangement options.
Implementation of this project is expected to improve railway infrastructure in terms of costs, operations, reliability, punctuality, increased capacity and energy efficiency, and reduced life cycle costs.
The MAT4RAIL project began in 2017 and was coordinated by CIDETEC (San Sebastián, Spain). Collaborators in the project included AIMPLAS and fifteen other research centers, SMEs, companies and universities from seven European countries: Instituto Tecnológico de Aragón (Spain), the University of Bremen (Germany), IMA Material Research and Application Technology GmbH (Germany), NVGTR GBR (Germany), Grammar Railway Interior GmbH (Germany), Centre Scientifique and Technique de L’Industrie Textile Belge (Belgium), Coexpair SA (Belgium), Huntsman Advanced Materials GmbH (Switzerland), Escatec Switzerland AG (Switzerland), Accelopment AG (Switzerland), Rise Research Institutes of Sweden AB (Sweden), ASAS Aluminyum Sanayi Ve Ticaret Anonim Sirketi (Turkey), Spirit Design Innovation and Brand GmbH (Austria) and INDAT Modellbau Werkzeugbau Formenbau GmbH (Austria).
The MAT4RAIL project was funded by the Shift2Rail Joint Undertaking (S2R JU), a public-private partnership in the rail sector established under the European Union Research and Innovation program Horizon 2020, grant agreement number 777595.
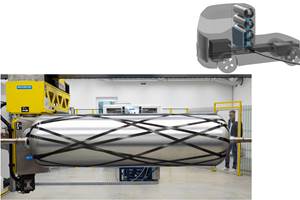
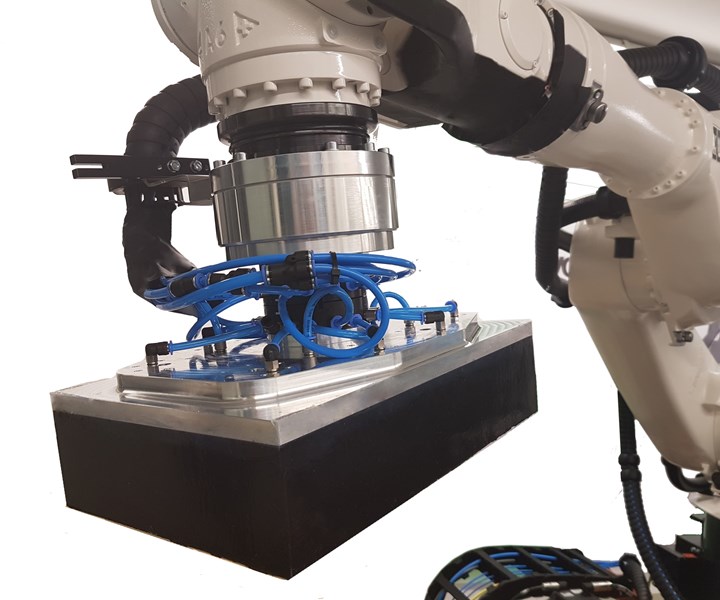
Cevotec scales up Fiber Patch Placement technology for large aerostructures
The SAMBA Step L automated fiber placement system can place patches of material up to 50 times larger than previous FPP systems.

Source | Cevotec
Automation specialist Cevotec (Munich, Germany), known for its Fiber Patch Placement (FPP) technology, has announced advancements in FPP to meet aerospace industry demands for complex and large aerostructures. The SAMBA Step L is the largest member of Cevotec’s SAMBA series to date, and can reportedly handle a maximum patch size of 200 millimeters by 300 millimeters, a scaling of 50 times compared to the initial 20-millimeter by 60-millimeter patch area. According to Cevotec, the new technology will widely expand the range of components processable by Fiber Patch Placement technology, with the primary goal of serving the aerospace industry’s application and process development requirements.
The SAMBA Step L is set up in the company’s cevoLab near Munich, Germany, and will be operational for customers this spring. The system features a 6-axis pick-&-place robot mounted on a linear axis.
“The increased range of the robot allows us to deal with specific part sizes of common aircraft components,” says Dr. Neven Majic, executive VP of Cevotec.“Adapted to the specific component sizes, we also scaled the patch grippers to process patches up to DIN-A4 size (approx. 200 millimeters by 300 millimeters).”
To enable maximum flexibility in the development process, predefined patches of different sizes and materials can be fed individually to designated pick-up positions. A smooth deposition of large patches on curved surfaces is realized by a special roll-placement feature. This new patch deposition strategy is said to contribute significantly to the quality of large patch laminates and to effectively prevent laminate air enclosures.
SAMBA Step L is designed for developing automated lay-up processes for large aerostructures, such as spatially curved sandwich structures, with sizes of up to 2 meters by 3 meters, and including materials like carbon, glass and aramid fibers, adhesives and more. Like other SAMBA systems, SAMBA Step L features a self-corrective, real-time process and placement control for constant laminate quality. This control system is said to ensure high precision of the placement and the exact repeatability between one part and the next. In addition, a force sensor has been implemented to precisely control compaction pressures during the placement process.
“Since we introduced the concept in 2018, various projects with aerospace customers have given rise to the idea of scaling up big time – relating to both patch and component sizes. And big time means 50 times as of today – we might go even larger in the future,” says Dr. Neven Majic, executive VP of Cevotec.
“With SAMBA Step L, we are taking a big step forward in our efforts to establish Fiber Patch Placement as standard production technology in the aerospace industry,” says Thorsten Groene, CEO of Cevotec. “We see applications in fairings, nacelles, panels, radomes and many more. The abilities to precisely place auxiliary materials of sandwich structures directly on the core, and remove intermediate debulking steps from the process, prove to be very promising in realizing lower cost structures for the next generation of complex aerostructures.”
FACC receives CAAC Part-145 maintenance certification
With CCAC certification, FACC can now offer its maintenance, repair and modification services to Chinese airlines.

Source | FACC
Aerospace group FACC (Ried/Innkreis, Austria) reported on Jan. 16 that the Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC) has granted FACC approval as a maintenance organization according to Part-145. FACC says that this CAAC certification represents a milestone for its aftermarkets services business segment, adding to its current list of certifications from the European EASA, the U.S. FAA and the Canadian TCCA. With this step, FACC is now offering airlines in the growing Chinese market a comprehensive range of maintenance, repair and modification services.
The approval process of the Chinese aviation authority CAAC lasted one and a half years, FACC says. The company is now authorized to perform maintenance work on components and systems operating under Chinese registration. In Austria, there is only one other company besides FACC that has been awarded CAAC Part-145 approval.
FACC’s Aftermarkets Services segment relies on three main pillars: repair, refurbish and replace. The company’s maintenance and repair services include structural repairs as well as those for engine and interior areas.
The three FACC divisions, Aerostructures, Engines & Nacelles and Cabin Interiors, are supported by the Aftermarket Services with expanded solutions. Aftermarkets services complements FACC’s core business of development and production of lightweight components for the global aerospace industry.
“This certification issued by the Chinese aviation authority marks a great success for FACC and is the result of hard work and the combined effort of all parties involved,” says Robert Machtlinger, CEO of FACC. “The strong growth in air traffic is also increasing the demand for qualified maintenance facilities in China. With this CAAC approval, FACC has established an excellent position for itself, and the good ratings in the approval process underline our high level of quality, expertise and reliability. We therefore possess the ideal prerequisites for successfully positioning ourselves as a maintenance company in this emerging market.”
SAMPE 2020 announces keynote speaker
Airbus Americas Vice President for Research and Technology Amanda Simpson will present on May 5 at SAMPE 2020 in Seattle, Wash., U.S.

The Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering (SAMPE, Diamond Bar, Calif., U.S.) has announced that Amanda Simpson, vice president of research and technology at Airbus Americas (Herndon, Va., U.S.), will be the keynote presenter at the SAMPE 2020 Conference & Exhibition to be held May 4-7, 2020 in Seattle, Wash., U.S.
According to SAMPE’s website, Simpson will present on Tuesday, May 5 from 8:00 to 9:30 a.m. She was named the Vice President for Research and Technology at Airbus Americas in June 2018, responsible for coordinating external research activities for Airbus in the United States.
Simpson will offer a retrospective on her 40-year career in aerospace and technology to identify some antiquated manufacturing processes still in use today and examine whether we are effectively preparing ourselves for an increasingly automation-dependent future in manufacturing and production.
She joined Airbus following government assignments in the United States Department of Defense. She was the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Operational Energy, responsible for developing the strategy for the utilization of energy for military operational forces worldwide, and was the senior advisor to the Secretary of Defense for all matters pertaining to energy in our military. Prior to accepting that responsibility, she was the Executive Director of the U.S. Army Office of Energy Initiatives, an organization developing large-scale renewable energy projects to bring energy security to Army installations leveraging private sector financing.
Previously, Simpson was the Special Assistant to the Army Acquisition Executive. In that role she was a principal advisor to the Assistant Secretary of the Army (Acquisition, Logistics and Technology) on all matters relating to Army acquisition, procurement, research & development and logistics. In 2010, Simpson was appointed by President Barack Obama to the position of Senior Technical Adviser to the U.S. Department of Commerce where she advised on policy and export control issues necessary to protect the security of the United States.
Simpson has been the recipient of numerous awards and recognitions including the 2004 Tucson YWCA Woman on the Move, 2005 Arizona Human Rights Fund Individual Award, the 2015 National Conference for College Women Student Leaders Women of Distinction Award, and was named an Outstanding Alumnus of Harvey Mudd College in 2018. She is a recipient of the Secretary of Defense Medal for Outstanding Public Service and the Department of Defense Pride Civilian Leadership Award. She is a nationally renowned speaker and has presented at corporations, government agencies, civic organizations, conferences and colleges around the country on gender and diversity.
Simpson holds both an Airline Transport Pilot certificate and a Certified Flight Instructor license, and has logged nearly 3,000 hours of flying in more than 60 different types of aircraft including float planes, flying boats, unmanned drones and multi-engine jets.
For more information about SAMPE 2020 and to register, go to www.sampeamerica.org.
Related Content
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Resin matrices for composites
The matrix binds the fiber reinforcement, gives the composite component its shape and determines its surface quality. A composite matrix may be a polymer, ceramic, metal or carbon. Here’s a guide to selection.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
From the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)


















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)