Chemical simulation to achieve sustainable composite materials testing
A collaboration between Molydyn, Bitzrez and the AMRC target the development of a viscosity modeling capability for quicker and more sustainable materials design.
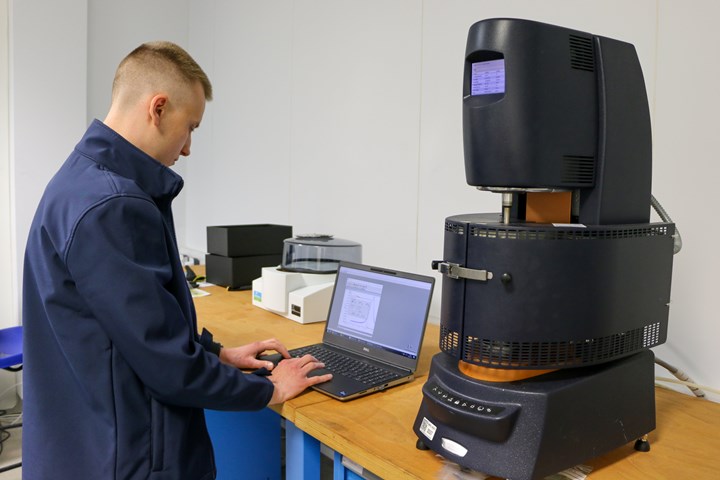

Development engineer for composites at the AMRC, Alex Brahinets, tests for material viscosity. Photo Credit: AMRC
Software company Molydyn (Bristol, U.K.) is to use chemical simulation to test new composite materials, in collaboration with the University of Sheffield Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC, Catcliffe, U.K.) and Bitrez Ltd. (Wigan, U.K.), a designer and manufacturer of specialist polymers and resins, in order to make the testing process more sustainable.
The project aims to use molecular modeling to develop a viscosity modeling capability for Molydyn’s accessible web simulation platform, Atlas, to help design better composite materials while reducing costs and environmental impact. Built upon previous collaborations with the AMRC, the project is funded by an Innovate UK Transformative Technologies grant.
Chemical simulation enables researchers to test new materials quickly with virtual experiments, screening out the prospects that are unfit for the lab. This saves laboratories time and money, while proving to be a more sustainable method — as no disposable gloves, single-use plastics or solvents are needed to test materials virtually.
With the rising price of electricity and raw materials, composite material manufacturers are feeling the pinch as high-pressure pumps and heating are often needed to infuse viscous, honey-like resin into the fibers. However, Molydyn, AMRC and Bitrez believe that resin tested for an optimized viscosity would flow like water and reduce the cost, environmental impact and difficulty of manufacturing composite parts.
“It’s good to be back working with the AMRC again, and tackling a major problem like viscosity,” Matthew Bone, CEO at Molydyn, says. “We’re hoping to expand Atlas and can give materials scientists a tool to help them design better composite materials. Composites are shaking up many sectors with the environmental benefits of lightweighting, so we’re keen to help get better composites to market faster.”
The AMRC, part of the High Value Manufacturing (HVM) Catapult network of research centers, will conduct empirical lab testing from its innovation cluster in Rotherham, U.K. Using its knowledge of working with composite materials, the AMRC will characterize the same set of polymers Molydyn is simulating, to act as a validation data set for current, and future, simulation research. Creating a broad dataset of viscosity measurements will give Molydyn an extensive pool to simulate and explore.
Chemical simulation enables researchers to test new materials quickly with virtual experiments.
Development engineer for composites at the AMRC, Alex Brahinets, says this project is expected to provide more detailed insight into material simulation by testing Atlas-designed formulations in the lab, and, in turn, using physical testing results to verify virtual simulation. “From our experience, a material’s processability can be a decisive factor in selecting suitable material for a customer’s application,” Brahinets adds. “For thermoset resins, the right viscosity is critical since it determines a material’s processability via common methods like infusion or resin transfer molding [RTM]. That is why predicting viscosity is essential for designing a new generation of sustainable materials.”
Bitrez is contributing to the project with a range of polymer formulations for testing and simulating. This includes a number of its popular bio-based materials, helping Molydyn to showcase how simulation performs on the next-generation of sustainable polymers. Working with commercial formulations will help to prove how capable modern chemical simulation is for real-world materials.
“We are always looking for opportunities to contribute and support the scientific community, and in turn, changing the face of industrial practice and rectifying anthropogenic damage,” Paul H. Jones, managing director of Bitrez, says. “We are pushing boundaries with disruptive, bio-based polymers and assisting in this project to aid efficient conversion of our matrix systems. Working with Molydyn and the AMRC is a pleasure and complements our sustainable development goals.”
Related Content
Carbon fiber in pressure vessels for hydrogen
The emerging H2 economy drives tank development for aircraft, ships and gas transport.
Read MorePlant tour: Dowty Propellers, Gloucester, U.K.
Transforming decades of design and RTM production reliability into more sustainable, next-generation composite propellers.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Resin matrices for composites
The matrix binds the fiber reinforcement, gives the composite component its shape and determines its surface quality. A composite matrix may be a polymer, ceramic, metal or carbon. Here’s a guide to selection.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Composites fibers and resins
Compared to legacy materials like steel, aluminum, iron and titanium, composites are still coming of age, and only just now are being better understood by design and manufacturing engineers. However, composites’ physical properties — combined with unbeatable light weight — make them undeniably attractive.
Read MoreRead Next
Thermosets vs. thermoplastics: Is the battle over?
Dale Brosius, the chief commercialization officer for the Institute for Advanced Composites Manufacturing Innovation (IACMI) and a regular CW columnist, sees a shift in the industry from infighting between proponents of thermoset and thermoplastic composites to a healthier competitive atmosphere that serves to make composites overall more competitive with legacy materials.
Read MoreUsing machine learning to accelerate composites processing simulation
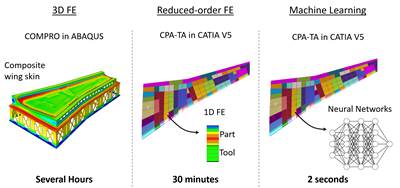
A speed gain of 1,000 to 10,000 times greater than traditional FE models has been achieved using machine learning models, enabling near real-time simulation for large composite components.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More








.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)