Toray announces growth, investment in carbon fiber composite materials
As part of its 2023-2025 management strategy, Toray projects 42% growth for pressure vessels, 30% growth in carbon fiber composite materials revenue and a doubling of capital investment.
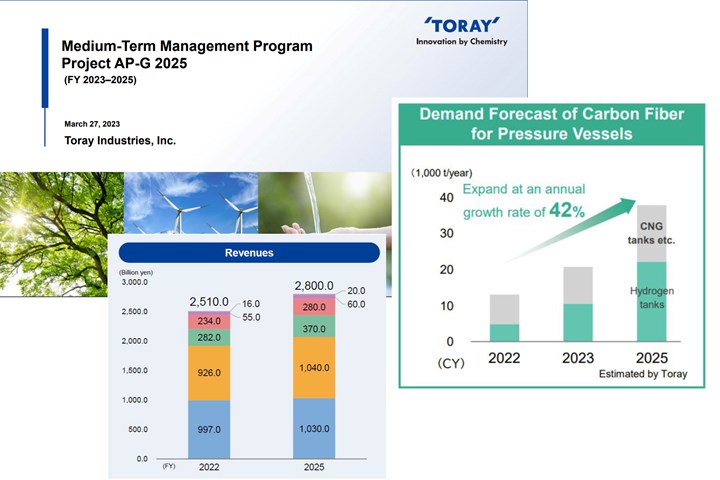
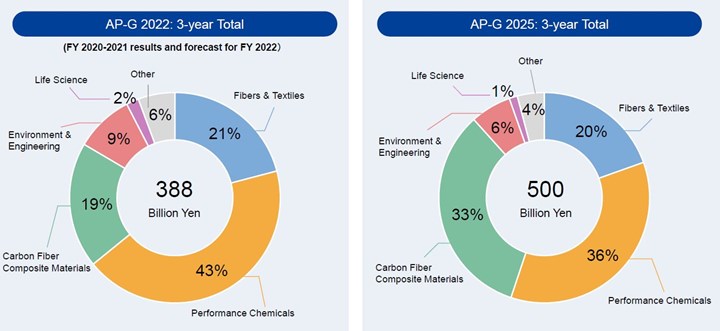
Toray Industries Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) has released its “Mid-Term Management Program, Project AP-G 2025” document outlining its corporate strategy for FY 2023-2025. In it, Toray outlines its vision for delivering innovative technologies and advanced materials to provide solutions to global challenges including sustainability. Out of the company’s 2.51 billion yen ($19 billion) in revenue for 2022, its Carbon Fiber Composite Materials business ranks third behind Fibers & Textiles and Performance Chemicals, contributing 282 billion yen ($2 billion).
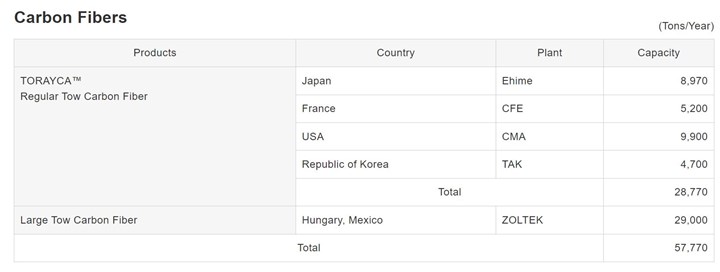
Toray carbon fiber production capacity. Photo Credit: Toray
Toray is reportedly the world’s leading manufacturer of carbon fiber, with a capacity to produce almost 58,000 tons of regular tow and large tow carbon fiber via plants in Japan, France, Korea, Hungary, Mexico and the U.S. In addition, Toray reportedly controls more than 50% of the global polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber market — historically more than two pounds of PAN is required to produce 1 pound of carbon fiber.
Toray also sells prepregs and thermoplastic composite materials through its Toray Advanced Composites (Nijverdal, Netherlands and Morgan Hills, Calif., U.S.) subsidiary.
Growth in FCEVs, pressure vessels
Toray notes strong sales of carbon fiber into wind turbine blades as the demand for renewable energy increases but also that it is developing a range of materials for production, transport, storage and use of hydrogen as a fuel. These materials include catalyst-coated membrane (CCM) which traditionally has used a carbon fiber support for the catalyst layer due to its high strength and low weight. Toray announced on March 17, 2023 that it would triple CCM production capacity at its subsidiary Greenerity (Alzenau, Bavaria, Germany), adding a third factory and expanding capacity of the second factory.
Through Grennerity, Toray also produces membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) for fuel cells in hydrogen-powered fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) including buses, trucks, commercial vehicles and passenger cars. An MEA comprises a proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membrane, catalyst layer and gas diffusion layers (GDL) which are made from graphitized carbon fiber-based nonwovens called carbon sheets, plates or paper (CP). At full capacity, Greenerity’s second plant will support annual production of more than 10,000 fuel cell vehicles.
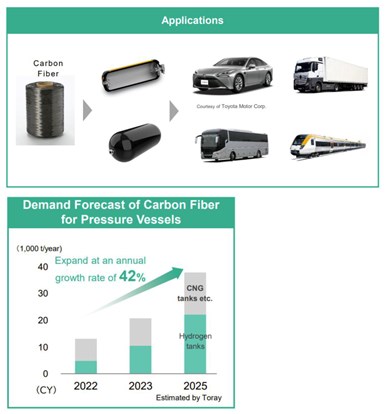
Growing demand for carbon fiber in pressure vessels. Photo Credit: Toray, Slide 23, AP-G 2025 strategy document.
Toray also notes that it supplies high-strength carbon fiber and liner resins for high-pressure hydrogen tanks. In fact, Toray T700S standard modulus fiber has become the benchmark for Type IV tanks storing compressed gas hydrogen (CGH2) at standard pressures of 350 and 700 bar for FCEVs. Toray projects that demand for carbon fiber in Type IV tanks will increase by 42% to almost 40,000 tons/year by 2025, including the traditional market for compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles and the new market for CGH2 tanks for FCEVs.
Growth in CF composites revenue, capital investment
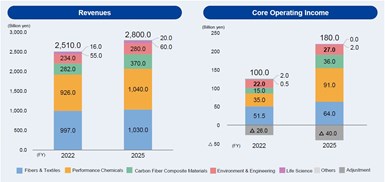
Toray projects growth in revenue for its Carbon Fiber Composite Materials business from a forecast 282 billion yen ($2.1 billion) in 2022 to 370 billion yen ($2.8 billion) in 2025. It will seek to maintain its market leader position by:
Growth in carbon fiber composites revenue and capital investment. Photo Credit: Toray, Slides 51-52, AP-G 2025 strategy document.
(1) Capturing recovering aircraft demand.
(2) Enhancing profit structure by improving profitability in industrial applications.
(3) Capturing expanding markets based on large-scale capital investment and expanding its business in wind turbine blades and fuel cell vehicles (tanks and electrode substrates).
(4) Serving mobility fields such as urban air mobility (UAM), where growing demand is expected in the future.
(5) Improving quality of carbon fiber products.
Toray will also increase its capital investment in carbon fiber composites, which had a 3-year total of 74 billion yen ($560 million) in 2022 but will more than double to total 165 billion yen ($1.25 billion) for the 3-year period ending in 2025.
Creating new materials, lowering costs via digitization
Accelerating new materials with machine informatics and artificial intelligence. Photo Credit: Toray, Slide 35, AP-G 2025 strategy document.
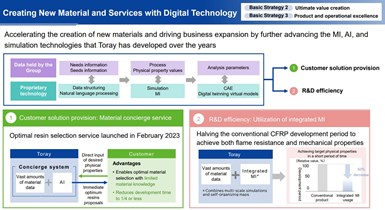
Another key part of Toray’s 2023-2025 strategy is to accelerate the creation of new materials and drive business expansion by advancing machine informatics (MI), artificial intelligence (AI) and digital simulation technologies that Toray has developed.
In September 2022, Toray announced a new digital service leveraging AI to predict physical property data to help its customers optimize resin choices and speed up product development. In November 2021, Toray announced it had developed a new carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) composite leveraging MI technology to swiftly achieve an exceptional combination of mechanical performance combined with flame retardance featuring a 35% lower heat release rate. The company explained that MI is a technique to streamline materials development by combining machine learning, theoretical density, simulations and databases. Further:
“As a part of its digital transformation initiatives, which draw on data and digital technologies to become more competitive, Toray deployed materials informatics in CFRP engineering and established a technology to develop materials swiftly by harnessing inverse problem analysis to refine materials designs based on the properties required. The company used a self-organizing map deployed in joint research with Tohoku University. A self-organizing map is an analysis technique that clusters high-dimensional data using unsupervised machine learning and represents it in a lower dimensional map to identify the essential structure hidden in the high-dimensional data. Toray was thus able, from a handful of experiments, to identify suitable combinations from a range of materials groups to achieve the desired properties … successfully engineering a matrix resin for CFRP and quickly developing a prepreg (the intermediate material of CFRP).”
In the AP-G 2025 strategy, Toray aims to use such digital technologies to enhance its value creation capability and competitiveness with a focus on:
New material and service creation
- Advance and develop simulation and informatics technologies.
- Combine material analysis, molding/chemical engineering analysis and simulation technology.
Manufacturing cost reduction and quality improvement
- Improve production efficiency using advanced process monitoring and data analysis.
- Raise the level of supply chain management using production planning simulation.
Related Content
Fiberglass Cutting Operation at Hubbell’s Lenoir City Plant Moves to Automation
Automating fabric cutting operations saves Hubbell Lenoir City money and can produce composite products faster at less cost to support infrastructure expansion.
Read MorePlant tour: Sekisui Aerospace, Orange City, Iowa, Renton and Sumner, Wash., U.S.
Veteran composites sites use kaizen and innovation culture to expand thermoplastic serial production, 4.0 digitization and new technology for diversified new markets.
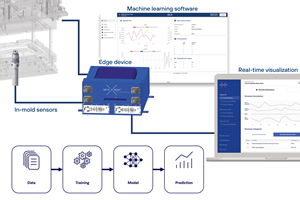
Read MoreNext-gen composites manufacturing: Combining material, machine and mold cavity data with analytics
Using a sensor, an edge device and machine learning software, sensXPERT sees into processes and is improving quality and cutting scrap, cycle time and energy use for composites customers like ZF and Carbon Revolution.
Read MoreThermoplastic composites welding: Process control, certification, crack arresters and surface prep
More widespread use of welded composite structures within a decade? Yes, but further developments are needed.
Read MoreRead Next
Toray achieves NADCAP accreditation for thermoplastic prepreg manufacture
Toray reported to be the first composites company to receive the Non-Metallic Materials Manufacturing – Thermoplastic Prepreg Manufacturing AC7124/6 certification.
Read MoreToray establishes new research facility fostering sustainable manufacturing innovation
Nagoya-based facility will be a hub for customer and academia collaboration and global R&D to accelerate Toray’s green transformation and explore advanced materials for myriad advanced mobility applications.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read More