CompoTech, Bilsing carbon fiber gondola beam development key for simplifying tooling management
Stiffer EOAT design for automotive tandem press line tooling increases load capacity and productivity, overcomes strokes per minute limitation and improves factory interchangeability.

Carbon fiber gondola beam for EOAT. Photo Credit, all images: CompoTech PLUS
The latest development project between CompoTech PLUS (Sušice, Czechia) and Bilsing Automation (Attendorn, Germany) has produced a new carbon fiber composite end of arm tooling (EOAT) on a six-axis robot for an automotive tandem press line using suction cup tooling. This type of EOAT is typically called a gondola beam due to its geometry, two symmetrical square beams attached to a flat central body. The arms holding the suction cups are attached to the gondola beam by means of tooling nests.
The collaborative project was initiated by a leading automotive body panel producer looking for a custom design alternative gondola beam to replace an existing hybrid aluminium-carbon fiber composite beam. The key objective for the project team was to simplify tooling management by developing a stiffer, longer EOAT that could provide the desired interchangeability of standard suction cup tooling nests throughout the factory.
The novel “all-carbon fiber”’ 2.6-meter long, low-profile gondola beam design has reportedly enabled highly beneficial standardization of the one touch adaptor (OTA) tooling nests across the factory between the different types of EOAT being used. Consequently, tooling nest assembly times and OTA related maintenance, parts and storage costs have all been halved.
Major production benefits from the project include a higher load capacity and improved productivity, overcoming the original hybrid metal-composite gondola’s nine strokes per minute limitation. The stiffer all-composite gondola has created the possibility that press lines could now be operated more than 75% faster at up to 16 strokes per minute, according to CompoTech.
CompoTech says it has proven design and production expertise in creating innovative carbon fiber composite machine tool and automation solutions to replace steel and aluminum. Using proprietary automated fiber laying (AFL) technology, CompoTech is able to offer stiffer and lighter alternative production components with better natural frequency damping, which increase productivity while reducing overall manufacturing costs.
Bilsing Automation is known for automotive stamping, bodyshop EOAT tooling and the development of modular industrial tooling systems. The company reportedly has a leading position in automated tooling using carbon fiber composites, collaboratively developed and manufactured by CompoTech.
Gondola upgrade design parameters
CompoTech developed a new laminate design using two types of carbon fibers to meet the required design parameters for a standardised EOAT for tandem press lines in the factory. The design specification was based upon actual factory press line generated data. The carbon fiber/epoxy laminate for each section of the new gondola uses a combination of both polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fabric and axial pitch fibers, precisely placed where needed using its AFL technology.
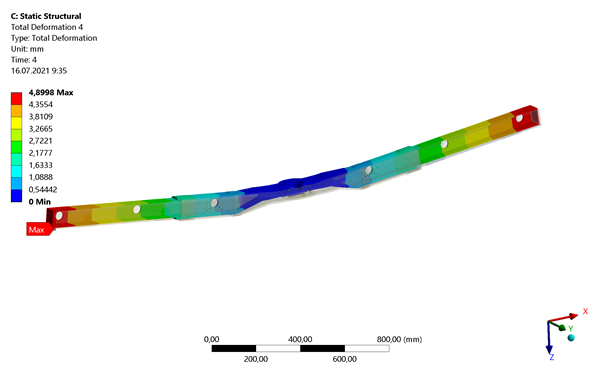
The gondola upgrade has an overall width of 2.6 meters, is required to handle a payload of up to 100 kilograms (~220 pounds) and can operate at 2G (~20 square meters per second) acceleration with minimal deformation, in both vertical and horizontal (perpendicular to beam axis) directions. The low-profile structure minimizes press opening, reducing process time when mounted below a linear axis, CompoTech says. Here, the linear motion is a custom seventh axis of the six-axis tandem feeder robot arms installed on existing press lines, for faster, more efficient panel transfer and extended reach.
Carbon fiber technologies
The carbon fiber gondola beam is made up of three sections: Two hollow square carbon fiber beam (80 x 80 millimeter) sections, with a tapered central carbon fiber body section molded in two halves (top and bottom). The individual three sections are then bonded together and overwound with additional fibers at key load areas for added reinforcement. The complete composite gondola beam weighs only 14 kilograms (~31 pounds), CompoTech claims. Once assembled, with the quick tool change fitting and the standard suction cup tooling nests mounted, the fully operational EOAT weighs 35 kilograms (~77 pounds).

Axial pitch fiber placed on PAN fiber fabric.
Each section uses both unidirectional (UD) high modulus axial ‘pitch’ carbon fibers and high-strength PAN fibers, with different laminate layup combinations in the top, bottom and sides. Composite pads are bonded at key points along the structural beams and machined to provide a precise surface for the assembly of the EOAT tooling nest. Dynamic load testing of the fully assembled carbon fiber gondola confirmed the high stiffness of the laminate system with a maximum deformation of only 4.9 millimeters.
“The challenge was to design the gondola with the central part having a similar bending stiffness as the 80- x 80-millimeter profile beams and avoid areas of stress concentration,” notes Gabriel Martinot, CompoTech’ lead design engineer. He explains how the company approached the project to meet all the design parameters. “UD pitch fibers were to compensate the geometrical loss of stiffness. We created ultra-high modulus carbon fabric preforms for the central body to achieve this. Our AFP [automated fiber placement] process enables us to automatically and precisely stack XN-80 UD pitch fibers on top of the PAN fabric to combine zero-degree axial ‘pitch’ carbon fibers with a standard ±45-degree PAN fabric. This provided the highest stiffness in the central beam exactly where needed.”
Gabriel goes on to explain about the other fabrication stages of the new design: “The central body halves and the two square beam sections were all first bonded together and then placed back into the AFL machine, which wound additional 90-degree carbon fibers to further reinforce where the beam is most loaded. This ensures reliable long-term performance under even the heaviest loads and significantly reduces any risk of crack propagation between the gondola sub assembly components.”
The project and experience gained in machine building and automation, is now being used in other industries such as defense, transport, agriculture, cycling and leisure marine.
Related Content
Composite rebar for future infrastructure
GFRP eliminates risk of corrosion and increases durability fourfold for reinforced concrete that meets future demands as traffic, urbanization and extreme weather increase.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MorePlant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MorePlant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
Read MoreRead Next
CW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read More







.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)


















