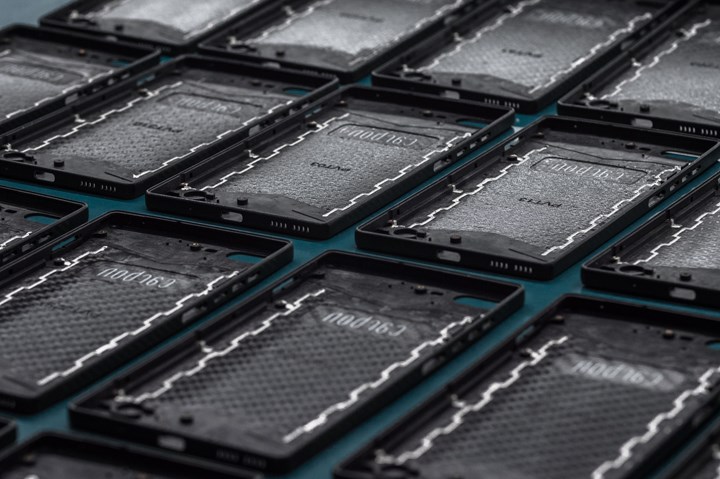
Carbon Mobile, SABIC to develop, deploy advanced carbon fiber in connected devices
Collaboration aims to deliver the next generation of thinner, lighter, stronger and more sustainable composite materials used in consumer electronics and automotive industries.
Carbon Mobile (Berlin, Germany), a deep-tech startup that develops radio-enabled carbon fiber composites in electronics devices, and chemicals company SABIC (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia), have entered into a strategic collaboration to drive industry-wide adoption of next-gen, advanced carbon fiber composites in devices. The collaboration, which was established by SABIC Ventures, will enable Carbon Mobile to leverage SABIC’s polymers portfolio, advanced research and development (R&D), testing and production facilities to deploy, at scale, new advanced materials, powered by Carbon Mobile’s HyRECM technology, which are in high demand among consumer electronics and automotive OEMs.
This new collaboration aims to develop a new joint material portfolio that is said will be more sustainable and future-proof by leveraging SABIC’s existing Trucircle materials and specific expertise in producing certified post-industrial recycled (PIR), post-consumer recycled (PCR) and certified bio-based feedstock.
“The consumer electronics industry is under a constant trend of miniaturization such as low weight or low thickness of devices with high screen,” Lina Prada, director, polymer application development and industry solutions SABIC, says. “Current material solutions are sometimes limited in mechanical performance. At SABIC, we are looking to new material solutions based on engineering thermoplastics systems. Working together with Carbon Mobile on composites and hybrid designs based on those materials can help us to achieve current unmet needs for miniaturization. Additionally, using our SABIC Trucircle solutions in those consumer electronic applications can help the industry to reduce its CO2 footprint.”
Advanced carbon fiber composites have long been sought after as lighter, thinner, stronger and more sustainable alternatives to materials currently used in connected devices. However, for more than a decade, industry leaders have been trying to solve the electrical and wireless connectivity issues, which block carbon fiber from being used in electronics and connected devices. Carbon Mobile’s patented HyRECM technology stabilizes the electrical and wireless connectivity properties of the composite without compromising on other material properties or the production process. This includes embedded electrostatic discharge (ESD) isolation, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and antenna noise cancelation, and also enables radio frequency (RF) signal permeation for low- and high-frequency bands in a single carbon fiber composite monocoque structure inside connected devices. The result is new design latitudes for the next generation of connected devices, unlocking new form factors, reducing the number of parts and complex assembly and eventually cost reduction.
“We believe Carbon Mobile can support the next generation of thinner, lighter and more sustainable connected devices,” Mahari Tjahjadi, business leader electrical and electronics at SABIC, adds. “Carbon Mobile is set to disrupt the lightweight electronics industry through its HyRECM material-enabling technology. With SABIC’s support, we expect to open up multiple sectors from wearables to automotive sectors and offer OEMs the more sustainable and high-performing solutions they demand.”
In March 2021, Carbon Mobile launched the Carbon 1 MK II, a carbon fiber smartphone which demonstrated the company’s patented HyRECM technology is feasible and mass production scalable. The new technology produces a robust carbon fiber composite monocoque housing structure for a very thin and light smartphone, with the least amount of material used as possible. To further boost the device’s connectivity, a conductive ink trace is integrated into the carbon fiber structure to stabilize the electrical and wireless properties. It weighed just 125 grams, making it 33% lighter than the average competitor, the company notes. Presented to the industry as the future standard of connected devices, the Carbon 1 garnered industry acclaim, picking up a Red Dot and JEC Design award. Now, Carbon Mobile is ready to bring its tech to all products in the consumer electronics and automotive industries. Carbon Mobile has already signed and is working with Tier OEMs to develop devices for product launches in 2023 and 2024.
“The tech industry has always strived for miniaturization but also are becoming aware of the need for more sustainable material alternatives to achieve it,” Firas Khalifeh, CEO of Carbon Mobile, says. “Our partnership with SABIC is born out of a common goal to help the planet, and so we’re excited that our OEM partners share our vision for a greener future with HyRECM technology as the enabler.”
Related Content
Materials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MoreCycling forward with bike frame materials and processes
Fine-tuning of conventional materials and processes characterizes today’s CFRP bicycle frame manufacturing, whether in the large factories of Asia or at reshored facilities in North America and Europe. Thermoplastic resins and automated processes are on the horizon, though likely years away from high-volume production levels.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fibers for composites
The structural properties of composite materials are derived primarily from the fiber reinforcement. Fiber types, their manufacture, their uses and the end-market applications in which they find most use are described.
Read MoreToray rCF from Boeing 787 is incorporated into ultra-light laptops
Torayca-based aerospace components have successfully been repurposed into the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 12, highlighting the ongoing application of recycled composites.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites for structural batteries
Researchers in Sweden find carbon fiber composites can be used for creating structural batteries that could help minimize mass in EVs and consumer electronics.
Read MoreCarbon Mobile relocates smartphone production to Germany
Carbon Mobile’s Carbon 1 MK II, a carbon fiber, plastic-neutral smartphone, aims to close the gap on e-waste.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More