VeeloHEAT Caul enables in-situ hot debulking capabilities
Built on existing debulk bagging procedures, Veelo Technologies’ debulking solution can take place at the tool during layup, reducing costs and improving throughput.
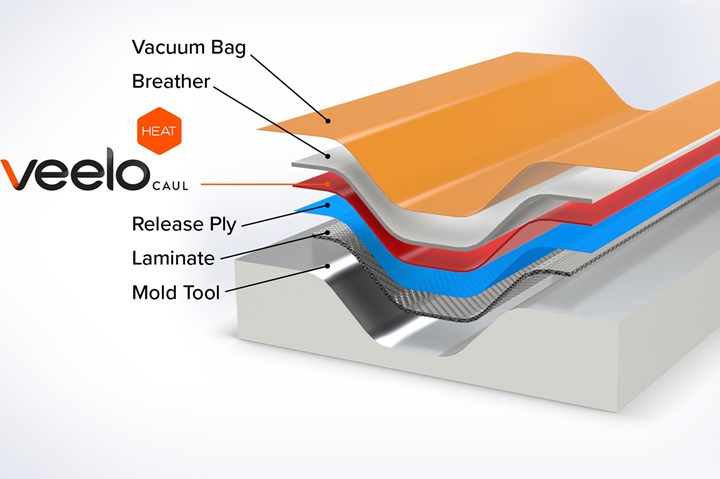
Photo Credit: Veelo Technologies
Veelo Technologies (Cincinnati, Ohio, U.S.) leverages its heat technology capabilities to help manufacturers stay out of the autoclave and oven by offering a complete composites debulking system, the VeeloHEAT Caul. A lightweight heating solution that builds on existing debulk bagging procedures, the system enables effective and reliable in-situ hot debulk, eliminating the need to transport parts to an autoclave or oven. Debulking can take place at the tool during layup, substantially improving throughput and build rates, thus reducing overall manufacturing costs.
Due to its flexible and pliable design, the durable and damage-resistant caul is highly uniform across large surface areas and can easily accommodate custom shapes and large tools. It features an FKM-based heater system for high performance and material compatibility. In addition to fatigue resistance, and a temperature range between 100ºF-400ºF, the system is also electrically efficient, with faster heating and cooling capabilities.
The caul is also controlled by the VeeloHEAT Controller, a cost-effective solution capable of controlling up to 16 zones or more. The digital IoT controller is capable of storing data and receiving updates locally or via the cloud and is highly customizable.
Applications may include out-of-oven heated debulk, out-of-autoclave composite processing, accelerated cure in autoclave processing, net-shaped composite repair, secondarily-bonded heater for metallic tooling and secondarily-bonded heater for electrothermal de-icing.
Related Content
-
From the CW Archives: Airbus A400M cargo door
The inaugural CW From the Archives revisits Sara Black’s 2007 story on out-of-autoclave infusion used to fabricate the massive composite upper cargo door for the Airbus A400M military airlifter.
-
Materials & Processes: Tooling for composites
Composite parts are formed in molds, also known as tools. Tools can be made from virtually any material. The material type, shape and complexity depend upon the part and length of production run. Here's a short summary of the issues involved in electing and making tools.
-
Novel dry tape for liquid molded composites
MTorres seeks to enable next-gen aircraft and open new markets for composites with low-cost, high-permeability tapes and versatile, high-speed production lines.












