Gordon Murray Automotive designs composite supercar
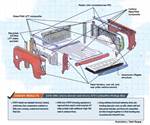
The T.50 vehicle design includes a carbon fiber composite chassis and body panels.

Source | Gordon Murray Automotive
Gordon Murray Automotive (Surrey, U.K.), a sister-business of vehicle design and engineering company Gordon Murray Design, has announced details of its first vehicle, the T.50 supercar. Conceived as the successor to the Murray-designed McLaren F1, the T.50 is designed with a carbon fiber composite chassis and body and is said to be the lightest supercar to be built.
Full production and customer deliveries for the T.50 are set for early 2022. The engineering planning, as well as the interior and exterior styling of the new vehicle, has been carried out by Gordon Murray Design. It will be manufactured by Gordon Murray Automotive at its new facility in Surrey, U.K. All major components will be bespoke and U.K.-sourced, including the powertrain, body and chassis.
The company says the key to producing the world’s lightest, most driver-focused supercar is the use of advanced carbon fiber engineering, as well as a deadication to minimize weight in every component. “This is the key to achieving enhanced performance and dynamics, and refocusing the supercar on the driver and the thrill of driving,” says Professor Gordon Murray CBE, chairman of Gordon Murray Group.
Composites are incorporated throughout the T.50 design, including a chassis built from a handmade sandwich-panel carbon fiber monocoque, carbon fiber composite body panels, and carbon-ceramic brakes.
The T.50 supercar reportedly will weigh 980 kilograms, making it approximately a third lighter than the average supercar. The external proportions are also highly compact — smaller than the footprint of a Porsche 911 at just 4,380 millimeters long and 1,850 millimeters wide — in order to to optimize handling, while still allowing space to comfortably fit three passengers plus luggage.
Related Content
-
Materials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
-
Materials & Processes: Resin matrices for composites
The matrix binds the fiber reinforcement, gives the composite component its shape and determines its surface quality. A composite matrix may be a polymer, ceramic, metal or carbon. Here’s a guide to selection.
-
Protecting EV motors more efficiently
Motors for electric vehicles are expected to benefit from Trelleborg’s thermoplastic composite rotor sleeve design, which advances materials and processes to produce a lightweight, energy-efficient component.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)












.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)
