GE Renewable Energy to open new offshore wind blade manufacturing plant
The facility, located in Teesside, U.K., will address the U.K.’s offshore wind market needs and facilitate production of 107-meter-long blades beginning in 2023.
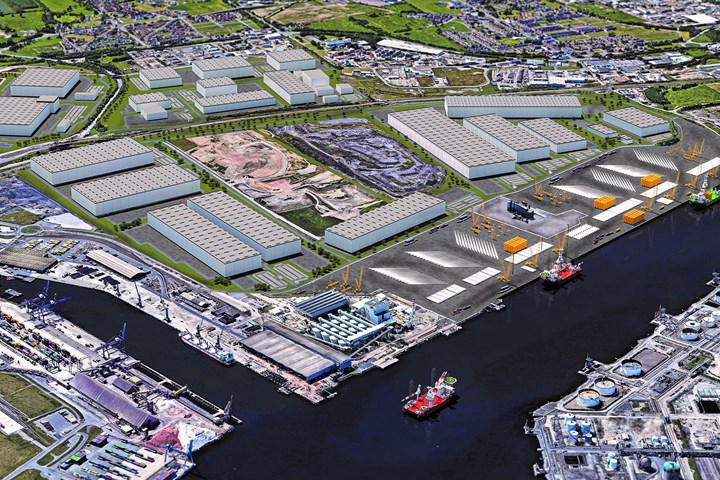

How Teesside will look following redevelopment. Photo Credit: Teesworks
GE Renewable Energy (Paris, France) announced on March 10 that it plans to open a new blade manufacturing facility in Teesside, a conurbation, or extended urban area, in northeastern England that has recently been designated as one of the U.K.’s newest freeports. LM Wind Power (Kolding, Denmark) plans to set up and operate this plant which will be dedicated to the production of its 107-meter-long offshore wind turbine blades, a key component of GE’s Haliade-X, said to be the most powerful offshore wind turbine in operation today. Terms of the construction and financing of the new plant are in advanced stages of negotiation between the interested parties.
GE Renewable Energy estimates that this new plant, set to open and start production of offshore wind turbine blades in 2023, could create up to 750 direct renewable energy jobs and up to 1,500 indirect jobs in the area to support the entire value chain needed to operate this facility. This announcement and commitment support the UK Government’s plan to develop jobs, infrastructure and supply chains to reach its goal to commission 40 gigwatts (GW) of offshore wind power by 2030 and become a global leader in green energy.
GE notes that this announcement is the result of strong partnerships built with key stakeholders such as the UK Government, the Tees Valley Mayor, Teesworks and its municipality.
“Teesside will continue to drive forward our green industrial revolution as we capitalize on new opportunities to produce clean energy through a brand new offshore wind port on the River Tees,” says U.K. Prime Minister Boris Johnson. “It will not only create thousands of jobs and harness the skills and expertise of this great industrial heartland, but also boost investment into the area as we build back greener.”
Hugh McNeal, CEO of Renewable UK adds: “GE Renewable Energy’s new blade turbine manufacturing plant will transform a former steelworks site on Teesside into a high-tech clean energy powerhouse, creating thousands of highly-skilled jobs in our U.K. supply chain. This announcement marks the start of the next generation of offshore wind manufacturing.”
The Dogger Bank Offshore Wind Farm, which is located between 125 and 290 kilometers off the east coast of Yorkshire, will reportedly benefit directly from the blades produced at this new plant. The three phases of the Dogger Bank Wind Farm, powered by GE’s Haliade-X offshore wind turbine, will have a combined installed generation capacity of 3.6 GW, enough to power six million U.K. homes. When complete in 2026, GE says, it will be the world’s largest offshore wind farm.

LM Wind Power’s 107-meter wind blade arriving in Blythe, U.K., for testing. Photo Credit: LM Wind Power.
“We’re incredibly proud to say Dogger Bank Wind Farm is the anchor project for the blade facility announcement by GE,” says Dogger Bank Wind Farm Project Director, Steve Wilson. “Dogger Bank Wind Farm is a world-leading development pushing the boundaries of offshore wind development and playing a key role in delivering the ambition to increase U.K. supply chain capacity and capability. Through our turbine supply order with GE, the Dogger Bank project is the catalyst for this important GE investment in Teesside, harnessing skills and expertise in the local area and delivering long-term benefits in the UK’s offshore wind sector.”
GE Renewable Energy says it already employs close to 1,500 people at its U.K. facilities, with the majority located between Stafford (GE Grid Solutions) and its LM Wind Power engineering center in Southampton. GE Renewable Energy has already announced an investment of $20 million in R&D and testing activities for its Haliade-X offshore wind platform — mainly in the U.K. — and continues to partner with ORE Catapult (Glasgow, U.K.) on areas such as innovation, R&D and testing major components. With this plant, the company is further expanding its renewable energy industrial footprint in the country and confirms its ambition to become a key actor in the offshore wind industry in this region. GE says it is also working closely with its suppliers to develop a local sourcing base in the U.K. for some critical components of offshore wind turbines.
Related Content
Recycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Composites fibers and resins
Compared to legacy materials like steel, aluminum, iron and titanium, composites are still coming of age, and only just now are being better understood by design and manufacturing engineers. However, composites’ physical properties — combined with unbeatable light weight — make them undeniably attractive.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fibers for composites
The structural properties of composite materials are derived primarily from the fiber reinforcement. Fiber types, their manufacture, their uses and the end-market applications in which they find most use are described.
Read MoreRead Next
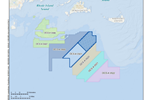
Vineyard Wind I offshore wind project poised for finalization
Bureau of Ocean Energy Management completes environmental analysis for proposed U.S. commercial-scale offshore wind farm with expectations to announce a decision by mid-2021.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More
















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)