Fill ACCUBOT spurs GKN Aerospace composite aircraft parts inspection
Flexible and precise multimodal robot system conducts quicker inspection processes, reducing GKN’s geometrical inspections from 11 hours to half an hour.
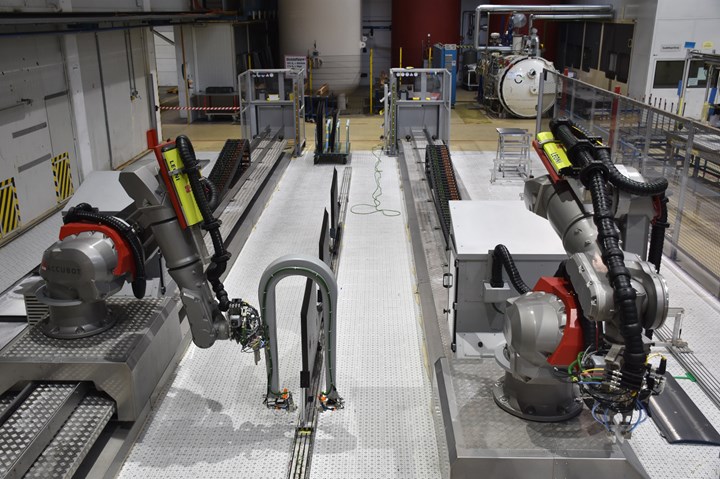

With two articulated robots on linear axes running in parallel, the ACCUBOT system from Fill can conduct non-destructive testing of composite components in three separate zones. All photo credit: P. Kemptner
Fill Gesellschaft m.b.H. (Gurten, Austria) announced on June 15 that the incorporation of its flexible and dynamic ACCUBOT (Accurate RoBot) multimodal robot system into GKN Aerospace’s (Redditch, U.K.) plant in Munich, Germany, which specializes in producing composite aircraft parts, enabled GKN to significantly increase the productivity and reliability of its non-destructive component testing (NDT).
As a leading supplier of components for the aircraft industry, GKN Aerospace produces aircraft parts exclusively from carbon fiber composite materials at its Munich plant. As aircraft components are safety-relevant, they are subject to the strictest quality requirements. GKN subjects 100% of the parts to an ultrasonic inspection in order to detect irregularities, such as inclusions of foreign matter, delamination or porosity. FILL reports that initial inspection times for NDT were as long as 100 minutes on the existing system.
The key criteria in the new tender for the NDT inspection system were a substantial reduction in inspection times and the option for other measurement and testing methods to be implemented on the system, in addition to the intrinsic ultrasonic inspection. Machine and plant engineering company, Fill, says it offered a solution with two articulated robots on linear axes running in parallel.

In ultrasound inspection by through-transmission, signals coupled by water jet must arrive at the receiver from the transmitter with less than 0.3-mm deviation.
According to Fill, ACCUBOT can inspect workpieces in three separate zones, and jointly in one of them. Automatic tool changing with the Fill FlexChange tool changer is said to enable tests to be conducted with different methods, such as phased array pulse-echo testing or through-transmission inspections with squirter technology, in one clamping operation. X-Ray, tomography, thermography and noncontact methods for geometry measurement can also be integrated in the system. Active Tool, an inspection head from Fill with an additional rotatory axis, enables through-transmission inspection in small, highly contorted areas.
Further, Fill says the system obtains its necessary absolute positioning accuracy through high-precision linear axes and additional rotary encoders fitted on the output side on the rotary axes of the ACCUBOT robots. A robot calibration system based on laser tracker helps achieve and maintain this high-precision subsequently.
Overall, ACCUBOT system incorporation has reduced the time required for annual geometrical inspections at GKN Aerospace from 11 hours to half an hour. The application-independent system software with the Fill STUDIO programming and operating environment has also reportedly brought significant gains in efficiency. It contains a digital twin of the entire system, enables offline programming of the robots during machine operation and features an augmented reality interface.
Fill notes that the system’s large efficiency gain results from significantly quicker inspection processes and the possibility to combine them automatically. “Alone with pulse-echo testing by means of phased array, the inspection time is reduced by 93%,” reports Dr.-Ing. Jakov Šekelja, head of Quality Management at GKN Aerospace Deutschland GmbH. “In addition, the several hours of tactile wall thickness measurement performed subsequently in the past now occurs automatically as a byproduct of the ultrasonic inspection.”
Related Content
Clemson Composites Center leads research in low-cost composite tooling
Innovative technology approach to use additive manufacturing and artificial intelligence to produce tools faster, at a lower cost and with less environmental impact.
Read MoreToray announces growth, investment in carbon fiber composite materials
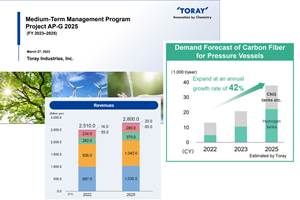
As part of its 2023-2025 management strategy, Toray projects 42% growth for pressure vessels, 30% growth in carbon fiber composite materials revenue and a doubling of capital investment.
Read MoreUltra high-rate composite deposition system trials to surpass layup targets
The NCC, alongside partners Loop Technology, Coriolis and Güdel, are on track to deliver dry fiber deposition rates exceeding 350 kilograms/hour, seven times more than standard aerospace rates.
Read MoreModular, robotic cells enable high-rate RTM using any material format
Airborne’s automated ply placement systems at Airbus, GKN Aerospace and Teijin Automotive Technologies aim to maximize flexibility and intelligent automation.
Read MoreRead Next
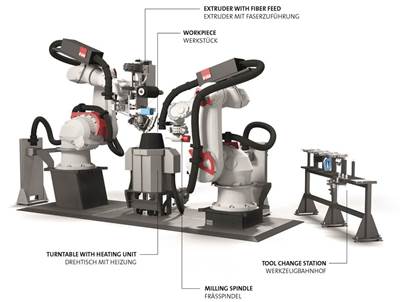
Fill ACCUBOT combines extrusion with continuous fiber additive capabilities
The system’s additive capability, augmented by subtraction via integrated robotic milling creates the potential for the production of cost-effective, high-performance and multifunctional composite components.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read More












.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)