CompositesWorld News for Jan. 16, 2020
Read news from BÜFA Composite Systems & Co. KG, Aliancys AG, Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering (SAMPE), Victrex Plc, EconCore, and Cygnet Texkimp
AOC Aliancys sells AOC Ltd. to BÜFA Composite Systems
Effective March 3, 2020, AOK (UK) Ltd. will operate under the name BÜFA Composites UK.

Source | AOC Aliancys.
AOC Aliancys (Schaffhausen, Switzerland, and Collierville, Tenn., U.S.) announces that effective March 3, 2020, subsidiary AOC (UK) Ltd (Manningtree, U.K.) will be acquired by resin supplier BÜFA Composite Systems (Rastede, Germany) and will operate under the name of BÜFA Composites UK. AOC Aliancys will remain the supplier of the resins portfolio.
AOC (UK) Ltd. has been a leading U.K. supplier of composites products with more than 25 years of experience in providing resin distribution and formulation services, and has been selling resins for the U.S.-based resin company AOC LLC. With the change in ownership, AOC (UK) Ltd. and the existing BÜFA Composites UK Distribution entity will be combined into one company.
“This acquisition will give our U.K. customers better access to quality products,” says Felix Thalmann, CEO of the BÜFA Group. “The new company will strengthen our capability to support our customers in the right way, and is a solid basis for their continued business growth.”
“BÜFA Composite Systems has been our long-standing partner for many years,” says Fons Harbers, vice president of marketing and sales EMEA at AOC Aliancys. “We are excited about the extended collaboration with BÜFA. We are confident that we will be able to provide our customers in the U.K. with an even better service as a result of the change.”
SAMPE 2020 announces keynote speaker
Airbus Americas Vice President for Research and Technology Amanda Simpson will present on May 5 at SAMPE 2020 in Seattle, Wash., U.S.

The Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering (SAMPE, Diamond Bar, Calif., U.S.) has announced that Amanda Simpson, vice president of research and technology at Airbus Americas (Herndon, Va., U.S.), will be the keynote presenter at the SAMPE 2020 Conference & Exhibition to be held May 4-7, 2020 in Seattle, Wash., U.S.
According to SAMPE’s website, Simpson will present on Tuesday, May 5 from 8:00 to 9:30 a.m. She was named the Vice President for Research and Technology at Airbus Americas in June 2018, responsible for coordinating external research activities for Airbus in the United States.
Simpson will offer a retrospective on her 40-year career in aerospace and technology to identify some antiquated manufacturing processes still in use today and examine whether we are effectively preparing ourselves for an increasingly automation-dependent future in manufacturing and production.
She joined Airbus following government assignments in the United States Department of Defense. She was the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Operational Energy, responsible for developing the strategy for the utilization of energy for military operational forces worldwide, and was the senior advisor to the Secretary of Defense for all matters pertaining to energy in our military. Prior to accepting that responsibility, she was the Executive Director of the U.S. Army Office of Energy Initiatives, an organization developing large-scale renewable energy projects to bring energy security to Army installations leveraging private sector financing.
Previously, Simpson was the Special Assistant to the Army Acquisition Executive. In that role she was a principal advisor to the Assistant Secretary of the Army (Acquisition, Logistics and Technology) on all matters relating to Army acquisition, procurement, research & development and logistics. In 2010, Simpson was appointed by President Barack Obama to the position of Senior Technical Adviser to the U.S. Department of Commerce where she advised on policy and export control issues necessary to protect the security of the United States.
Simpson has been the recipient of numerous awards and recognitions including the 2004 Tucson YWCA Woman on the Move, 2005 Arizona Human Rights Fund Individual Award, the 2015 National Conference for College Women Student Leaders Women of Distinction Award, and was named an Outstanding Alumnus of Harvey Mudd College in 2018. She is a recipient of the Secretary of Defense Medal for Outstanding Public Service and the Department of Defense Pride Civilian Leadership Award. She is a nationally renowned speaker and has presented at corporations, government agencies, civic organizations, conferences and colleges around the country on gender and diversity.
Simpson holds both an Airline Transport Pilot certificate and a Certified Flight Instructor license, and has logged nearly 3,000 hours of flying in more than 60 different types of aircraft including float planes, flying boats, unmanned drones and multi-engine jets.
For more information about SAMPE 2020 and to register, go to www.sampeamerica.org.
Victrex optimizes PAEK polymers for AM platform
The University of Exeter has commissioned an EOS P 810 laser sintering platform, for use with Victrex high-temperature PAEK polymers.
Source | Victrex
The University of Exeter’s (Exeter, U.K.) Centre for Additive Layer Manufacturing (CALM), in collaboration with Victrex (Cleveleys, U.K.), is one of the first to commission the recently launched EOS P 810 laser sintering additive manufacturing (AM) platform, for use with Victrex high-temperature polyaryletherketone (PAEK) polymers.
The goal of the partnership is to introduce next-generation Victrex PAEK polymers and composites while improving the performance of the underlying AM processes. The university says investment in the new EOS P 810 platform is expected to accelerate the commercialization of AM for high-performance parts.
“We can now further our research by utilizing the next generation of high temperature systems, the EOS P 810,” says Professor Oana Ghita, the lead of CALM at the University of Exeter. “The new equipment allows us to link the fundamental research with the commercial manufacturing process, to optimize the materials and their application, while accounting for the new thermal, optical and mechanical upgrades and providing us with accurate insights into the detailed dynamics of laser sintering.”
The EOS P 810, which has a build volume of 700 by 380 by 380 millimeters and two 70-watt lasers, is capable of printing with materials that have melting temperatures around 300°C. According to Victrex, it is suitable for the low-melting-point PAEK polymers the company has designed and optimized specifically for AM.
“This is an exciting milestone in our collaboration with the University of Exeter, which we announced in 2018, creating an effective eco-system to accelerate the commercialization of AM materials for performance parts to meet customer needs,” says Ian Smith, Victrex director of innovation.
Low & Bonar licenses EconCore’s thermoplastic honeycomb technology
Using EconCore’s honeycomb technology, Low & Bonar has developed a lightweight flooring underlay product designed with high acoustic properties.
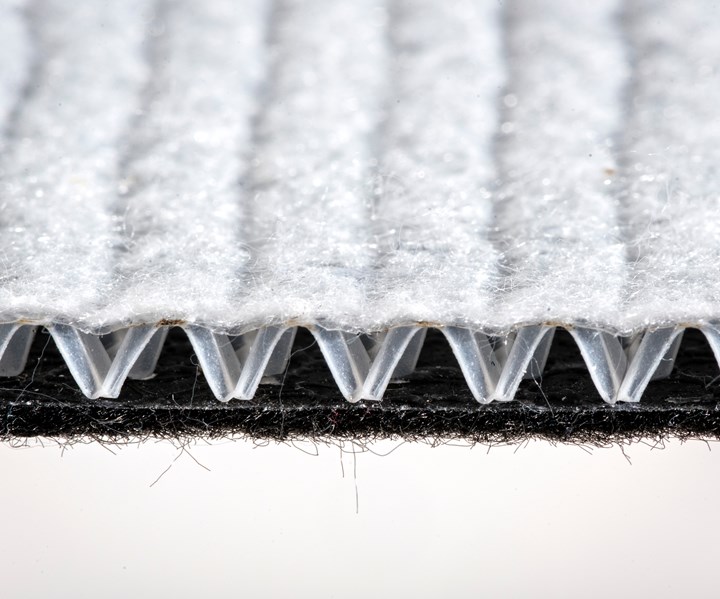

A close-up view of Colcore Sonic, showing the relaxed honeycomb core with non-woven performance fabrics. Source | Low & Bonar and EconCore
Advanced fabrics company Low & Bonar (London, U.K.) has signed a license agreement for the use of EconCore’s (Leuven, Belgium) thermoplastic honeycomb technology. At the Domotex trade show in Hannover, Germany (Jan. 10-13, 2020), Low & Bonar launched a new flooring flooring product using EconCore’s honeycomb technology.
The product, called Colcore Sonic, uses EconCore’s continuous, high-volume production process for lightweight thermoplastic honeycomb sandwich panels. Colcore Sonic is deliverable on a roll, rather than as a rigid panel, for easy handling, storage and installation, and it is said to be lightweight and thin while exhibiting strong soundproofing and high compression strength properties.
The new product concept was developed in 2018, followed by a series of testing, learning and further optimization. Relevant industry qualification tests were achieved to demonstrate the product meets and exceeds industry standards, Low & Bonar says.
Independent testing found that Colcore reduced impact sound by 20 decibels and airborne sound transmission is 57 decibels, both defined as the noise perceived in a room below. Radiated walking sound, defined as walking noise in the same room, registered at 56.4 Sone (a unit of loudness), considered to be a comfortable sound level. The results demonstrate that the product is ideal for flooring of both, commercial and residential buildings.
“Even with the latest generation of leveling compounds, preparing subfloors prior to the installation of vinyl click flooring is time-consuming. Unrolling, cutting and positioning this high-performance underlay system is all it takes to smooth out uneven surfaces in minutes rather than hours or days,” says Soon Joo Bovenschen, new technology manager at Low & Bonar.
“This license agreement and the subsequent successful product development is a result of intensive work and an excellent partnership between EconCore and Low & Bonar,” says Tomasz Czarnecki, chief operating officer at EconCore.
Cygnet Texkimp supplies high-capacity 3D weaving creel to the AMRC
The University of Sheffield’s Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC) will use the creel to help produce woven structures for automotive and aerospace applications.
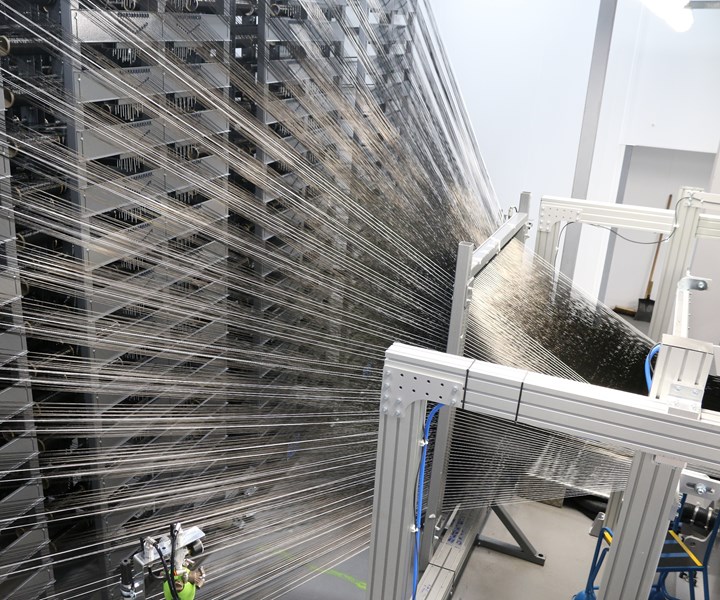

Source | Cygnet Texkimp
Custom machinery manufacturer and fiber processing specialist Cygnet Texkimp (Cheshire, U.K.) reported on Jan. 14 that it has supplied a 3,000-position 3D weaving creel to the Composites Centre at the University of Sheffield’s Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC, Sheffield, U.K.).
The high-capacity creel will be used alongside AMRC’s 3D jacquard loom to produce woven structures from carbon fiber, ceramic and other technical fibers for automotive and aerospace applications. With a footprint of fewer than 40 square meters, the 3D creel is said to be one of the highest volume-per-square-meter weaving creels in the world. It features an intelligent control system to maintain low and consistent running tension of the fiber into the downstream weaving process and to enable operators to adjust the tension of individual positions or zones according to fiber weight and position in the woven structure. A bespoke guide system accommodates varied fiber counts (k-counts) and tow widths, and a tension recuperation mechanism offsets the shedding motion of the loom.
“AMRC is taking dry fiber processing for composites to a new level in the U.K. Significant investment in advanced technologies will help the manufacturing sector develop composite solutions for wide ranging applications in automotive, aerospace, space and beyond,” says Chris McHugh, dry fiber development manager at the AMRC Composite Centre. “Controlling tension of fibers, varying speed of fibers and minimizing degradation to ensure highest performance is realized, are key factors that we need in our processes.”
“The way fibers are fed into the weaving process is absolutely vital to the quality of the finished product,” says Chris Furphy, product director at Cygnet Texkimp, “which means that fiber tension and fiber path — ensuring the fibers never come into contact with each other as this can easily cause damage — are really important when it comes to designing a creel like this.”
Cygnet Texkimp and the AMRC began working together in 2014. In 2018, AMRC commissioned Cygnet Texkimp to design a 2D weaving creel that is also housed at its facility.
Related Content
Materials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Composites fibers and resins
Compared to legacy materials like steel, aluminum, iron and titanium, composites are still coming of age, and only just now are being better understood by design and manufacturing engineers. However, composites’ physical properties — combined with unbeatable light weight — make them undeniably attractive.
Read MoreOne-piece, one-shot, 17-meter wing spar for high-rate aircraft manufacture
GKN Aerospace has spent the last five years developing materials strategies and resin transfer molding (RTM) for an aircraft trailing edge wing spar for the Airbus Wing of Tomorrow program.
Read MorePlant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
Read MoreRead Next
CW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)













.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)















