CompositesWorld News for Dec. 13, 2019
Read news from LeMond Carbon, GKN Aerospace, TRB Lightweight Structures, and Kaman Composites - Vermont
LeMond Carbon audits rapid-oxidation carbon fiber technology
A Bureau Veritas audit of LeMond Carbon’s carbon fiber, made with a novel rapid-oxidation technology, shows mechanical properties comparable to Toray T300 fiber.
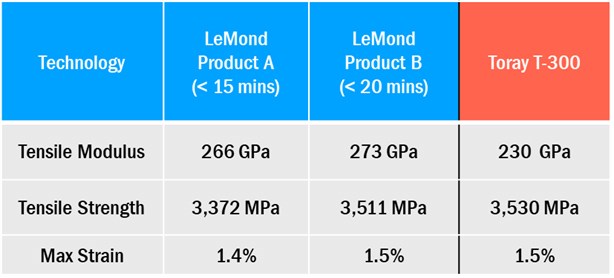
LeMond Carbon carbon fiber mechanical properties from Bureau Veritas audit. Source | LeMond
LeMond Carbon (Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.) announced on Dec. 12 the results of an independent technical audit conducted by Bureau Veritas (BV, Paris, France) of its rapid-oxidation carbon fiber manufacturing process. The audit was conducted on a pilot line at Deakin University’s Carbon Nexus facility in Geelong, Australia. LeMond says the total oxidation time and material properties verified by BV support LeMond’s claims to lower costs and significantly increased output versus traditional carbon fiber manufacturing technology.
Bureau Veritas offers laboratory testing, inspection and certification services and audits innovative technologies and manufacturing processes. For the audit of LeMond’s technology, BV measured total oxidation times of sub-15 and sub-20 minutes over two separate production campaigns of 24K standard modulus (SM) carbon fiber, achieving fiber tow properties in excess of 270 GPa tensile modulus and 3,500 MPa tensile strength (see table).
The BV audit was conducted on Carbon Nexus’s 100-metric-ton (nameplate) pilot line which is currently producing samples for trials with LeMond’s target customers in several SM industrial markets. In addition to accurately measuring oxidation times and assuring process traceability, BV oversaw the fiber sampling, packaging and shipping of audit samples for extensive testing at the BV laboratories in Pessac, France. Composite tow tests of the LeMond fiber were completed according to ASTM D 4018-17 standards.
LeMond and Deakin University are teamed to commercialize this rapid-oxidation technology, which enables reductions of 75% and 70% in capex and energy consumption per kilo of output respectively. LeMond says the rapid-oxidation process enables the company to produce carbon fiber with the lowest embodied energy of any standard PAN-based carbon fiber available today.
“This is a significant milestone for our company. Having our technology independently verified by BV validates the revolutionary nature of our technology,” says Greg LeMond, founder and chairman of the board of LeMond Carbon. “My team and I are excited to bring our high-performance, low-cost carbon fiber to the global market, and look forward to expanding into new markets where the current high cost of carbon fiber has been a significant barrier to adoption.”
“Deakin has always been excited about the potential of our patented new technology and it is encouraging to receive independent validation that our technology is effective at scale. We look forward to continuing to support LeMond as they commercialize a lower-cost and lower-emission carbon fiber,” says Derek Buckmaster, director Carbon Nexus.
Having proven the capability to successfully produce a competitive standard modulus carbon fiber, LeMond has launched a new capital campaign to develop a 5,400-metric-ton (nameplate) production facility in Oak Ridge. To date, parent LeMond Companies LLC has raised approximately US$18.6 million of seed capital from individual and institutional investors, including Deakin University
Founded in 2016, LeMond Carbon Inc. is commercializing carbon fiber manufacturing technology under a global 20-year license from Deakin University. It is currently operating a pilot scale carbon fiber manufacturing line located at Deakin University’s Carbon Nexus facility in Geelong, Australia. Upon expected commencement of operations in 2021, LeMond Carbon intends to produce and sell carbon fiber composite products to the wind, aerospace, oil and gas and auto industries.
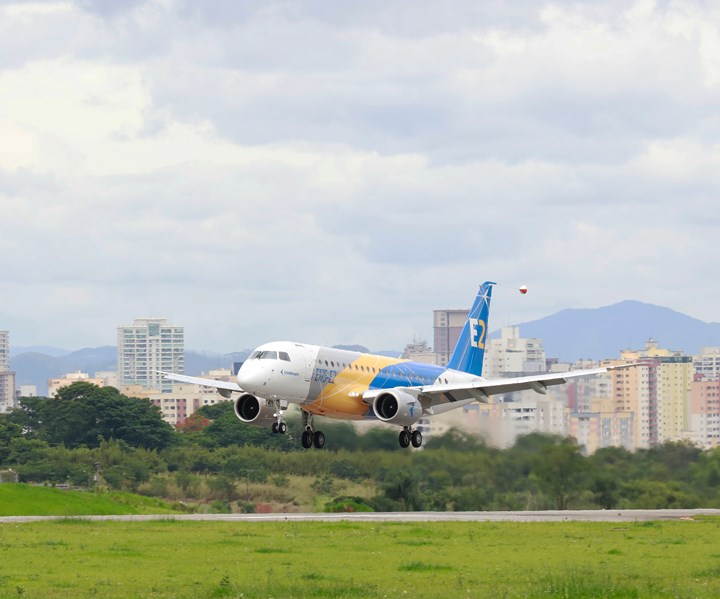
First E175-E2 jet completes maiden flight
The first of three prototypes on its way to certification, the composites-intensive Embraer E-175-E2 jet completed its first flight on Dec. 12.

Source | Embraer
The Embraer E175-E2 made its inaugural flight on Dec. 12 from the company’s facility in São José dos Campos, Brazil. Embraer reports that the maiden flight of the E175-E2, which is the third member of the E-Jets E2 family, kicks off a 24-month flight test campaign for the jet.
Composite parts on Embraer’s E-Jet family are said to include flight-control components such as flaps, ailerons, elevators, rudders and spoilers, as well as landing gear doors, wing-fuselage fairings and radomes.
The E175-E2 departed at 11:07 a.m. local time from the runway adjacent to Embraer’s Faria Lima complex and flew for two hours and 18 minutes. Embraer’s Captain Mozart Louzada commanded the aircraft along with first officer Wander Almodovar Golfetto, and flight engineers Gilberto Meira Cardoso and Mario Ito. The aircraft took off and landed with fly-by-wire (FBW) controls in normal mode. The crew evaluated aircraft performance, flight quality and systems behavior.

Source | Embraer
Embraer will use three aircraft for the E175-E2 certification campaign. The first and second prototypes will be used for aerodynamic, performance and system tests. The third prototype will be used to validate maintenance tasks and will be outfitted with interior furnishings.
The E175-E2 has one additional row of seats compared to the first-generation E175 and can be configured with 80 seats in two classes, or up to 90 in a single class. According to Embraer, the airplane will save up to 16% in fuel and 25% in maintenance costs per seat compared to the E175.
Embraer also reports that like the E190-E2 and the E195-E2, the E175-E2 will have the longest maintenance intervals in the single-aisle jet category with 10,000 flight hours for basic checks and no calendar limit for typical E-Jet operations.
The E175-E2 features new Pratt & Whitney GTF PW1700G ultra-high bypass ratio engines, a completely new wing, full fly-by-wire controls and new landing gear. Compared to the first-generation E175, 75% of aircraft systems are new.
“[The inaugural] flight of the E175-E2 marks the completion of our vision to produce a family of new-generation commercial aircraft that bring unparalleled cost savings to our customers, exceptional comfort for their passengers and fewer emissions for the planet,” says John Slattery, president and CEO of Embraer Commercial Aviation. “The E190-E2 and the E195-E2 are already stellar performers. The E175-E2 is just as impressive. We’re eager to get working on certification.”
GKN Aerospace named key supplier for Aerion Supersonic business jet
GKN Aerospace will design and develop the empennage and electrical wiring interconnection systems for the AS2.

Source | GKN Aerospace
Aerion Supersonic (Reno, Nev., U.S.), leader in supersonic technology, has that GKN Aerospace (Redditch, U.K.) will design the empennage and electrical wiring and interconnection systems (EWIS) for the AS2 supersonic business jet.
According to GKN Aerospace, design activities have already started on-site at Aerion in Reno, Nevada and in GKN Aerospace’s engineering centers in the Netherlands and Romania.
“We are excited to collaborate with Aerion and to support the preliminary design phase of this all-new supersonic AS2 business jet. As technology leaders in both electrical wiring interconnect system (EWIS) and business jet empennages, we can bring unrivaled knowledge and expertise to the project,” says John Pritchard, CEO of GKN Aerospace ASEA.
Aerion’s AS2 is reported to be the first privately built supersonic commercial aircraft. The 12-passenger business jet is scheduled to begin flight testing in 2024.
“Aligning with industry leading partners is key to making sustainable supersonic travel a reality,” says Tom Vice, Aerion CEO. “GKN Aerospace brings more than 100 years of aerospace development and extraordinary aerostructures expertise, including thermoplastic composites and electrical wiring systems, to our AS2 supersonic business aircraft.”
GKN Aerospace is a leading multi-technology Tier 1 aerospace supplier company, specializing in developing, building and supplying a range of advanced aerospace systems, components and technologies. See the company’s CompositesWorld showroom for more recent CW coverage.
TRB Lightweight Structures to open U.S. manufacturing facility
The facility in Richmond, Ky. will focus on high-volume production of automotive components using TRB’s robotics-assisted press-forming process.

Lexington, Kentucky. Source | TRB Lightweight Structures
TRB Lightweight Structures (TRB; Cambridgeshire, U.K.) has announced that it will soon be opening a composites manufacturing center in Richmond, Ky., U.S., as a joint venture with Toyota Tsusho America (New York, N.Y., U.S.). According to TRB, the 40,000-square-foot facility will be equipped with state-of-the-art robotics to allow high-volume production of carbon fiber components using TRB’s press-forming process.
The initial focus for the facility, TRB says, will be production of carbon fiber components for automotive applications, particularly for electric vehicles (EV). TRB says it has developed a production process that allows carbon fiber to be press-formed using advanced industrial robotics, allowing components to be manufactured at a similar price point to equivalent aluminum parts. The Richmond facility will complement TRB’s U.K. manufacturing operations, providing greater access to these materials for the North American market.
“We are delighted to announce the creation of TRB Lightweight Structures America together with Toyota Tsusho America. The U.K. is a global leader in composites, and we are very excited to bring our technology and expertise to the rapidly growing EV sector in the USA,” says Richard Holland, managing director of TRB.
Kaman Composites expands medical customer base
Kaman Composites will supply composite assemblies for Carestream Health’s line of digital radiography products.

Source | Kaman Composites
Kaman Composites – Vermont Inc. (KCV; Bennington, Vt., U.S.), a subsidiary of Kaman Corp., has announced an agreement to manufacture complex composite assemblies for Carestream Health’s (Rochester, N.Y., U.S.) DRX digital radiography product line.
All composite detail parts and assemblies will be manufactured and delivered from the KCV facility in Bennington, Vermont. Deliveries are expected to begin in 2020.
“Our in-house tooling and product design capabilities, coupled with our performance, allow us to provide the support our customers need when they look to increase market penetration at an accelerated pace,” says Alexander Gamble, general manager for Kaman Composites-Vermont. “This new relationship speaks to the value we provide to our customers, especially those in the demanding medical imaging segment.”
“This new customer win demonstrates the strength of Kaman’s composites capabilities to meet the rigorous requirements of the medical market. Our ability to deliver upon our commitments of quality, on-time delivery, and responsiveness allows us to attract the top customers across end markets who are looking to partner with leading manufacturers to provide solutions for their advanced composite requirements,” says Mark Withrow, vice president and general manager of Kaman Composites US.
Related Content
Aptera joins forces with C.P.C. Group to accelerate solar EV production
Specialized composite bodies are being produced in Modena, Italy, for Aptera’s BinC vehicle, enabling eventual manufacturing ramp-up of 40 vehicles/day to meet demand targets.
Read MoreMass, cost, durability improvements: EV battery enclosures, Part 2
As interest grows in composite battery covers and trays, composite materials suppliers work to meet current and future needs of automakers, battery module producers.
Read MoreProtecting EV motors more efficiently
Motors for electric vehicles are expected to benefit from Trelleborg’s thermoplastic composite rotor sleeve design, which advances materials and processes to produce a lightweight, energy-efficient component.
Read MoreHankuk, Carbon, Dymag partner to scale up manufacturing of state-of-the-art carbon fiber wheels
Hybrid-composite BX-F wheels will serve high-performance road cars, luxury EVs and large SUVs and pickups.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read More







.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)

















