AFRL, Boeing, Thermwood partner to develop low-cost, autoclave-capable tooling
The project is using Thermwood’s vertical, large-scale 3D printer to build a carbon fiber-reinforced demonstrator tool for an aircraft fuselage skin.
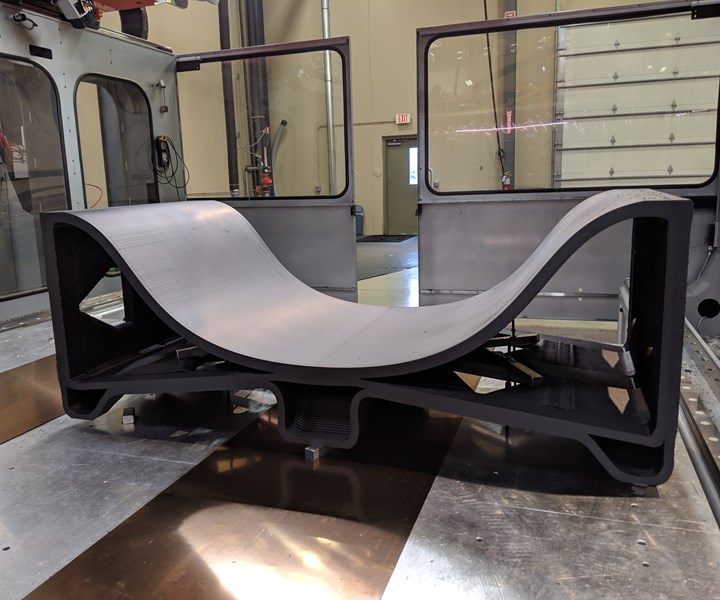

Source | Thermwood Corp.
Thermwood Corp. (Dale, Ind., U.S.) has announced that it is collaborating with the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL; Dayton, Ohio, U.S.) and Boeing (Chicago, Ill., U.S.) on a research program to produce low-cost responsive tooling using additive manufacturing.
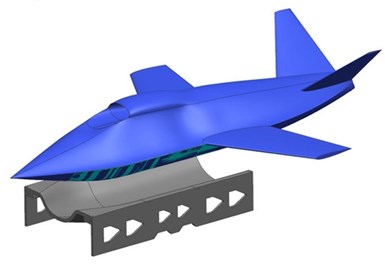
The concept for AFRL’s aircraft fuselage skin and tooling. Source | Thermwood Corp.
According to Thermwood, the initial demo tool is for an AFRL concept aircraft fuselage skin. The idea was submitted by Boeing to the AFRL’s Manufacturing and Industrial Technology Division (ManTech), which is interested in large-scale, polymer-based additively manufactured (AM) composite cure tooling.
For this project, Boeing contracted Thermwood to demonstrate the capability of its Large Scale Additive Manufacturing (LSAM) machine. Thermwood says this machine offers innovation through its Vertical Lay Print (VLP) capability, which 3D-prints layers perpendicularly to the floor (see more on this technology in “Thermwood’s vertical layer printing turns AM on its side” from sister publication Additive Manufacturing). With VLP, Thermwood says, components can be printed at larger sizes, reducing the assembly costs.
To validate the VLP process using high-temperature autoclave-capable materials, Boeing and AFRL decided to start by 3D-printing a mid-scale tool, which has the same width, height and bead path as the final tool, but has been shortened in length from 10 feet to only 4 feet.
The mid-scale tool was printed on Thermwood’s LSAM Additive Manufacturing Demonstration machine at its southern Indiana facility, using a 40-millimeter print core running 25% carbon fiber-reinforced polyethersulfone (PESU). According to Thermwood, this was the first high-temperature tool printed using the VLP system. The tool required 5 hours and 15 minutes to print, and the resulting part weighed 367 pounds. After final machining, the tool was probed for surface profile and tested for vacuum integrity. It passed room temperature vacuum test and achieved dimensional surface profile tolerances. The full-scale tool will weigh approximately 1,400 pounds and require 18 hours to print, Thermwood says.
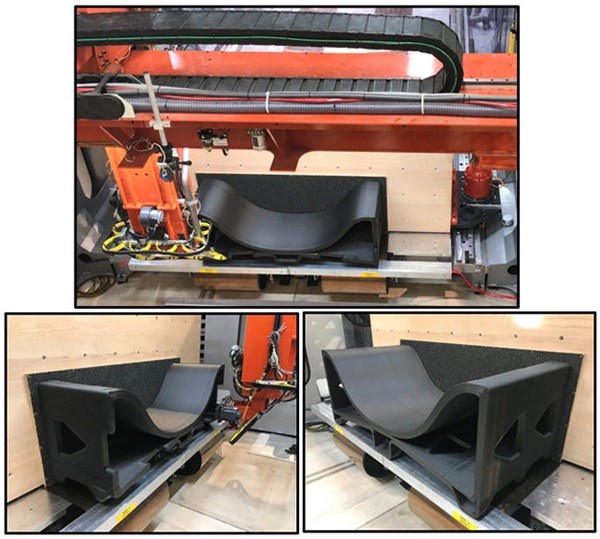

Source | Thermwood Corp.
AFRL’s Low-Cost Attritable Technology (LCAAT) program is looking at different tooling approaches with the goal of breaking the cost growth curve and fielding new systems faster. “We are interested in additively manufactured tooling’s ability to reduce the cost and time to procure autoclave capable tooling,” says Andrea Helbach, AFRL program manager. “Additionally, AM tooling supports changes in vehicle design with minimal non-recurring expenses.”
Related Content
-
Composite rebar for future infrastructure
GFRP eliminates risk of corrosion and increases durability fourfold for reinforced concrete that meets future demands as traffic, urbanization and extreme weather increase.
-
Materials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
-
Plant tour: Albany Engineered Composites, Rochester, N.H., U.S.
Efficient, high-quality, well-controlled composites manufacturing at volume is the mantra for this 3D weaving specialist.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)














