The making of the BMW i3
CompositesWorld's tour of the BMW i3 manufacturing and assembly plant in Leipzig, Germany, offers a glimpse of one possible future of automotive production.

The Life Module of the BMW i3 all-electric is comprised of resin transfer molded carbon fiber composite structures that are assembled via robotics at the company's manufacturing and assembly plant in Leipzig, Germany.
The composites industry is full of innovators and creative thinkers, people who move the industry forward incrementally toward greater efficiencies, lower costs and higher quality. But the big material and process leaps the composites community has seen throughout its history have required more than individual expertise. The Chevrolet Corvette or The Boeing Co.’s 787 Dreamliner, for example, is the product of a massive, collective corporate commitment, backed by a capital investment as big, bold and precedent-setting as the envisioned product — a commitment that, to some composites pessimists, appears reckless, hasty, ill-timed and doomed.
Corporate trailblazers are rare, and rarely attempt such leaps without a good command of the materials, processes and technologies required to achieve success. Even so, the risk of doom is real, and redoubles with the size of the enterprise. Missed deadlines and technical setbacks are all the more embarrassing for being so public — and inevitably exploited by naysayers. But at the end of what is, at best, a colossal controlled experiment is the honor and recognition as the first to reach a bold and audacious goal.
Onto this less-traveled corporate road the BMW Group steered when, in 2009, it elected to manufacture an all-electric, four-door passenger car using carbon fiber composites. Originally denoted the MegaCity Vehicle, the commuter car now known as the i3 is designed primarily for urban driving and can travel about 100 miles/160 km on a single charge.
As is widely known by now, the i3 features two primary structures, the aluminum Drive Module – which incorporates the powertrain, chassis, battery, and structural and crash functions – and the Life Module (passenger cell), made from carbon fiber composites. The latter is capped by a composite roof made with recycled carbon fiber, and features a spare but comfortable interior that also incorporates recycled materials and other composites made with natural fiber reinforcements.
We were invited in March to visit the i3 manufacturing and assembly plant in Leipzig, Germany and was offered a chance to see, firsthand, the materials and technologies employed in the creation of this unique vehicle. You will find, in the June issue of Composites Technology magazine, a full report on the facility, materials and processes.
In the meantime, some highlights and impressions from the tour:
- BMW, as might be expected, exerts strict control over the quality of carbon fiber produced and woven for the i3, starting at the SGL Automotive Carbon Fibers plant in Moses Lake, Wash., USA.
- Process control of the resin transfer molding (RTM) process used to make the carbon fiber structures for the Life Module is carefully managed. BMW uses, in Leipzig, seven Schuler presses for RTM, with two KraussMaffei RTM injection units on each press.
- BMW clearly is looking for opportunities to speed up its RTM process, reduce carbon fiber scrap rates and minimize resin usage. Thermoplastics are on the radar.
- The roof of the i3 makes creative use of carbon fiber scrap with the applicaiton of a stitched, nonwoven carbon fiber fabric made by SGL Group.
- Assembly of the Life Module — fully automated by 173 fully articulating ABB robots — is impressive. Only adhesive bonding is used, with no mechanical fasteners.
- BMW, when we visited, was making 70 i3 vehicles per day, which BMW says is on par with expectations — and expected to grow. With the i8 sports car (also with a carbon fiber Life Module) about to start production, the company's RTM throughput will be well tested.
- Driving the i3 is fun (see below image). It's smooth, peppy, quiet and responsive.

CompositesWorld conferences director Scott Stephenson (left) with editor Jeff Sloan (right) in front of the BMW i3 they drove while visiting the BMW Group manufacturing and assembly plant in Leipzig, Germany.
Related Content
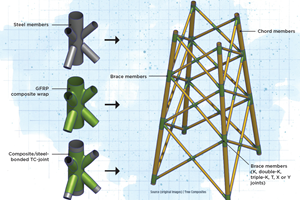
Novel composite technology replaces welded joints in tubular structures
The Tree Composites TC-joint replaces traditional welding in jacket foundations for offshore wind turbine generator applications, advancing the world’s quest for fast, sustainable energy deployment.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fibers for composites
The structural properties of composite materials are derived primarily from the fiber reinforcement. Fiber types, their manufacture, their uses and the end-market applications in which they find most use are described.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MorePEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More