Covestro to Showcase Novel 3D-Printed Shock Absorber
Printed in three materials using three different processes, this part also boasts a high degree of functionality.
A unique 3D-printed shock absorber will make its debut at the Fakuma 2018 trade fair (October 16-20) Friedrichshafen. For several years,Covestro (U.S. office in Pittsburgh) has been developing customized polymer materials for all common additive manufacturing processes. The diverse properties of these filaments, powders and liquid raw materials make them suitable for many applications in various industries.
At the upcoming trade show, Covestro will present a complex demonstrator for a shock absorber (Stand 4206, Hall B4)
According to the company, the part marks another milestone in the move from the creation of individual prototypes to the integration of various functions and mass production.
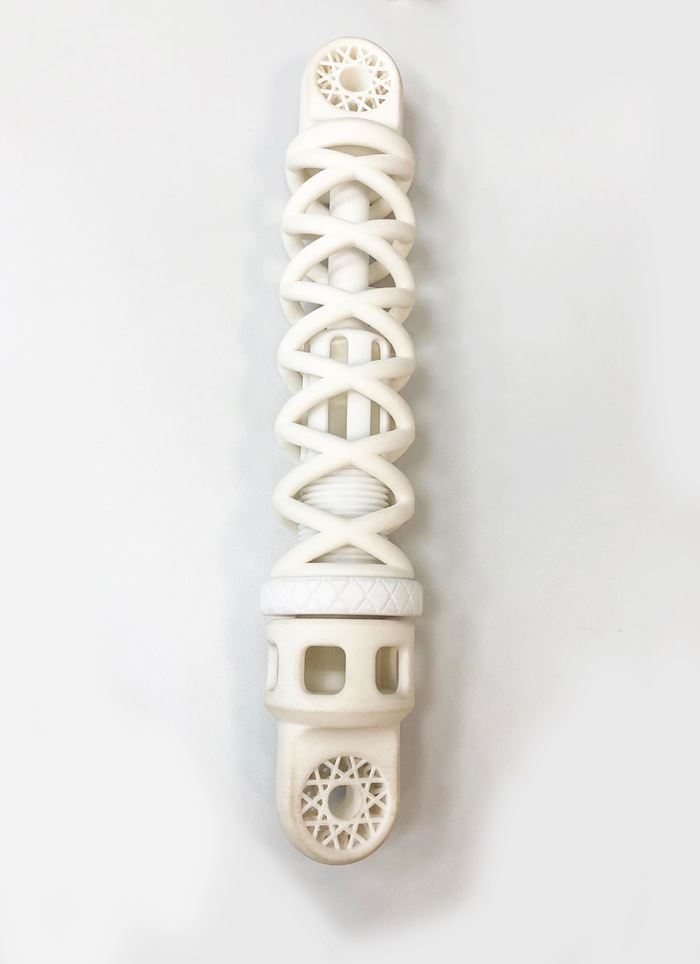
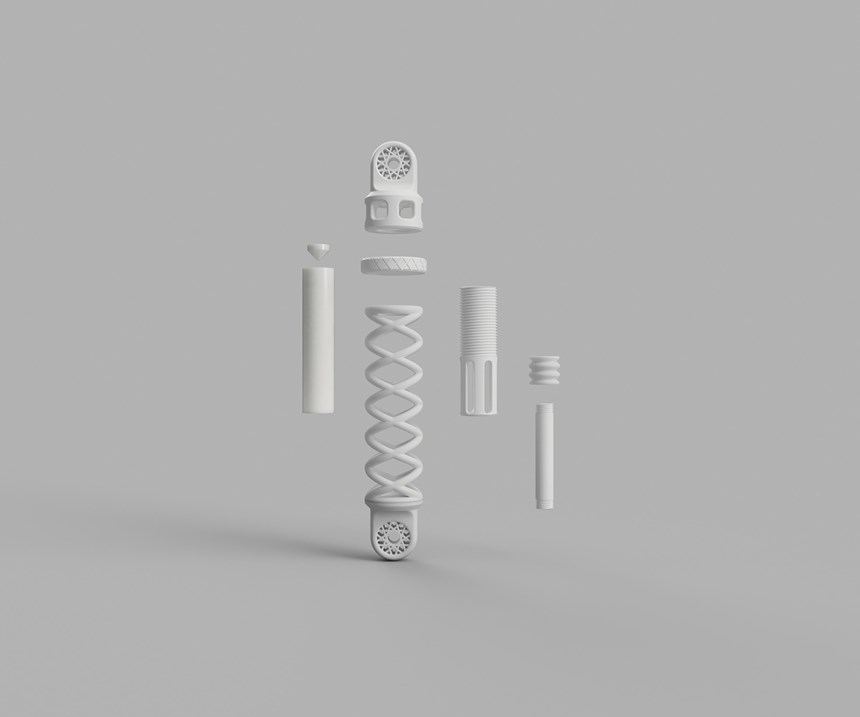
In addition to the high degree of functionality attributed to this shock absorber, it is unique in that the individual parts were produced from three different materials and with the aid of three different manufacturing processes.
The outer spring of the 40 x 7 cm (15.7 x 2.8 in) part is made of powdered TPU. It was shaped layer by layer using selective laser sintering (SLS) and is notable for its elasticity and high abrasion resistance.
The adjusting screw inside the shock absorber has to be very strong and hard. For this reason, it is made of filaments of Covestro's robust PC material, using the fused filament fabrication (FFF) process. The air chamber in the interior is created from a liquid PUR resin. The digital light processing method has proven itself for such components with filigree structures, as in this case as well.
The individual components are subsequently connected to each other. Explained Lukas Breuers, a marketing manager for 2D and 3D printing at Covestro, "This complex structure would not have been possible with conventional production processes. Another new development is the combination of different materials with various, tailor-made properties. This has enabled us to significantly expand the possibilities of additive production and its areas of application.” Other products from the company for additive manufacturing are characterized by good heat resistance, abrasion resistance or flexibility.
Related Content
-
Materials & Processes: Fibers for composites
The structural properties of composite materials are derived primarily from the fiber reinforcement. Fiber types, their manufacture, their uses and the end-market applications in which they find most use are described.
-
Materials & Processes: Resin matrices for composites
The matrix binds the fiber reinforcement, gives the composite component its shape and determines its surface quality. A composite matrix may be a polymer, ceramic, metal or carbon. Here’s a guide to selection.
-
Protecting EV motors more efficiently
Motors for electric vehicles are expected to benefit from Trelleborg’s thermoplastic composite rotor sleeve design, which advances materials and processes to produce a lightweight, energy-efficient component.