Composites give shape to new passenger bus
The VDL Bus & Coach Citea bus features composite structures fabricated using a vacuum expansion process (VEX) with specially formulated foaming resin compounds supplied by BÜFA Composite Systems.
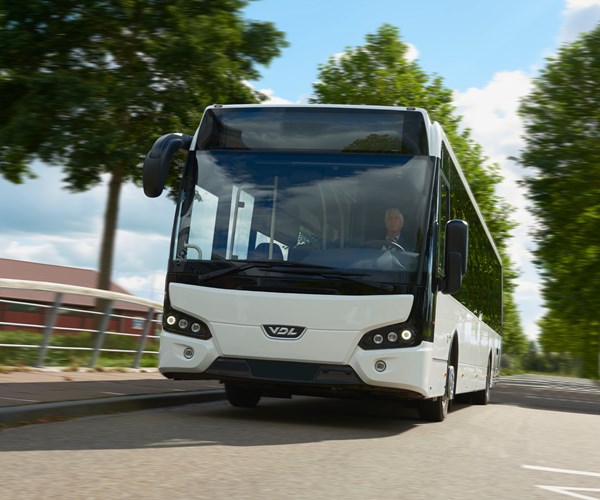

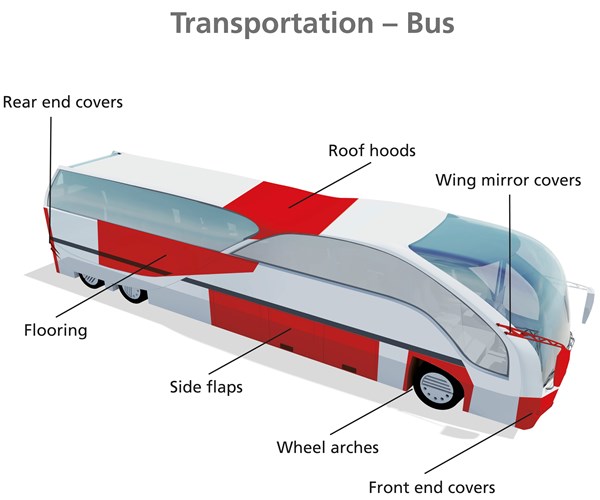
VDL Bus & Coach Citea passenger bus.
Passenger bus manufacturer, VDL Bus & Coach (Valkenswaard, The Netherlands), has introduced its new Citea series of busses to the market, incorporating multiple light-weight composite components. These components are made by applying a foaming resin formulation supplied by BÜFA Composite Systems (Rastede, Germany) using resin supplied by Aliancys (Schaffhausen, Switzerland).
VDL Bus & Coach has a reputation for use of incorporating a highly modular design in its products. This modular approach facilitates building custom-made busses, while simplifying bus repair, maintenance and spare parts supply. VDL already has a good experience using composites in its busses, but for the Citea bus, it wanted to step up its efforts in reducing weight and manufacturing efficiency for the medium-sized production series. The company had been looking for composite material technologies that better combine design flexibility, mechanical strength and light weight.
OMB Composites (Psáry, Czech Republic) made for VDL multiple composite components in a vacuum expansion process (VEX), working with specially formulated resin compounds supplied by BÜFA Composite Systems. In the VEX process, the mold surface is first covered with a gel coat. Then a dry fiber reinforcement is applied, followed by the the foaming resin. After closing the mold, the resin starts to foam and fill the mold. The below video demonstrates the process using an open mold.
Depending on part design and end-use performance requirements, the VEX-technology can make components as large as 2 by 6m. With weight savings up to 45% compared to parts made from conventional resin technologies, the technology reportedly enables cycle times of 3 hours per part. Use hand lay-up techniques, notes BÜFA, results in a much longer production time. With this new technology, part surface can be very smooth, enabling the application of surface coatings for a Class A finish. Use of the BÜFA Firestop Foaming Resin System, the company says it is also possible to improve fire protection and smoke development at a level typical for the rail transport industry.
When developing the special foaming resin compounds, BÜFA worked closely with Aliancys to fine-tune resin composition and cure. “Aliancys has a track record in the development of novel resins with unique chemistries and features. Together we were able to optimize the resin system, delivering the right performance in the final part,” comments Lothar Kempf, commercial director of BÜFA. “We know that the great resin consistency of the Aliancys resins helps to ensure that our customers’ processes are stable and predictable, so their part manufacturing process is very reliable.”
Aliancys says the orthophthalic base resin used for making the foaming resin compound was tailored by Aliancys to the specific needs of the application. “We like very much working together with our customers in the development of new process technologies,” comments Paul Vercoulen, CTO of Aliancys. “With this close collaboration, BÜFA and Aliancys have been able push the limits of composites part performance and processing, delivering light weight, sustainability and great system cost.”
Related Content
-
We're going to need a lot of propeller blades
As advanced air mobility expands and annual shipsets get into the thousands, the demand for composite propeller blades is expected to skyrocket. What are the implications for the composites supply chain?
-
Materials & Processes: Fibers for composites
The structural properties of composite materials are derived primarily from the fiber reinforcement. Fiber types, their manufacture, their uses and the end-market applications in which they find most use are described.
-
Composites end markets: Aerospace (2023)
With COVID in the past and passengers flying again, commercial aircraft production is ramping up. The aerocomposites supply chain is busy developing new M&P for an approaching next-generation aircraft program.
















