Recycled carbon fiber for lower-priced lightweight in heavy trucks?
Though its recent SuperTruck project used CFRP to slash over 3,200 lb, Volvo says it needs lower cost materials like recycled carbon fiber.
SOURCE: Inhabitat.com
Volvo Trucks USA (Greensboro, NC) unveiled its SuperTruck earlier this year — the third out of four SuperTruck vehicles in the US Dept. of Energy’s (DOE) $80 million program of the same name. Launched in 2009, the program aimed to develop Class 8 tractor trailers with 50% greater fuel efficiency. All four SuperTrucks used carbon fiber composites, though to varying degrees.

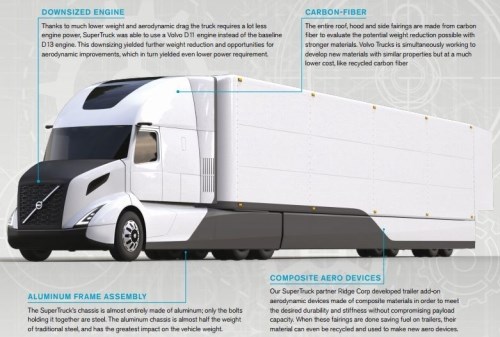
Enhancements that were developed on Volvo’s SuperTruck and then carried over to its production vehicles include a new aerodynamic bumper, flared chassis fairings and an aerodynamically enhanced roof. Volvo Trucks North America president Goran Nyberg said his company’s SuperTruck routinely achieved more than 12 mpg during testing while loaded and has now surpassed 13 mpg with some additional tinkering.
Lightweight materials played a significant role. For example, the aluminum trailer frame is 45% lighter than the 2009 production steel frame. According to senior project manager Pascal Amar, who oversaw this first SuperTruck project, designers didn’t just swap out steel for aluminum but instead designed the frame to take advantage of the lighter metal’s properties.
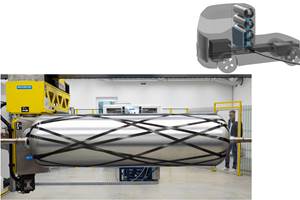
Composites also played a role. The roof, hood and side fairings are made from carbon fiber materials. According to Volvo Trucks USA’s webpage on the SuperTruck, aerodynamic trailer add-on fairings were developed and built by partner Ridge Corp. (Columbus, OH, US), maker of DymondPly and DymondGuard glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastic wall liners and Green Wing Aerodynamic Side Skirts. The SuperTruck fairings reportedly lower overall truck weight vs. 2009 models and minimize drag for dramatic fuel savings.
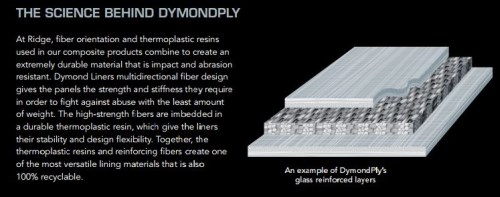
SOURCE: Ridge Corp.
The aluminum frame shaves 900 lb out of a total 4,700 lb weight loss, but the installation of new drivetrain technologies put back about 1,500 lb, resulting in a net weight savings of 3,200 lb.
Though Volvo depended on carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) to meet SuperTruck program goals, it says the material’s price tag is too high and it is working to develop new composite materials with similar properties at lower costs, like recycled carbon fiber.
Other SuperTrucks and CFRP
Navistar (Lisle, IL, US) was the last to unveil its SuperTruck, reportedly using CFRP in the cab’s upper body panels, roof, back panel and dash panel. Its partner Wabash National (Lafayette, IN, US) developed a lightweight trailer that cut 1525 lb. It also used an aluminum frame but added composite leaf springs to its design, as well as composite sidewalls, closures and support structure for the aerodynamic skirt.
Daimler Trucks North America and subsidiary Freightliner (Portland, OR, US) did not detail use of composites in their SuperTruck, except for carbon fiber cabinets in the cab. However, the team did specify a list of lightweighting partners including MSI-ACPT, Maxion Inmagusa (Castaños Municipality, Coahuila, Mexico), Oregon State University, Strick Trailers (Monroe, IN, US) and carbon fiber supplier Toray.
The Peterbilt (Denton, TX, US) and Cummins (Columbus, IN, US) supertruck reportedly featured CFRP in the front of the trailer skirts and the trailer front’s “horse collar”.
SuperTruck II
Building on the SuperTruck initiative’s success, DOE has announced SuperTruck II and selected the following four teams, each of which will receive $20 million in federal funding to be matched dollar-for-dollar by each recipient:
- Cummins will design and develop a new more-efficient engine and advanced drivetrain and vehicle technologies.
- Daimler Trucks North America will develop and demonstrate a tractor-trailer combination using a suite of technologies including active aerodynamics, cylinder deactivation, hybridization, and the electrification of accessories.
- Navistar will design and develop a vehicle and powertrain with electrified engine components that can enable higher engine efficiency and a significantly more aerodynamically reengineered cab.
- Volvo Technology of America will develop and demonstrate a tractor trailer combination with lightweight cab that achieves the freight efficiency goal using alternative engine designs and a variety of system technologies.
SuperTruck II projects will research, develop and demonstrate technologies to improve heavy-truck freight efficiency by more than 100%, relative to a manufacturer’s best-in-class 2009 truck, with an emphasis on technology cost-effectiveness and performance. Though SuperTruck II will build on lessons learned during the first project, it will produce completely new trucks.
Volvo Trucks’ Nyberg explained that because this second project requires truck makers to demonstrate a one- to two-year payback on technologies used, his company will have to eliminate some of the costlier systems that were deployed on the first SuperTruck. This requisite quick payback also suggests that more of the improvements that make the final cut will also proceed to production vehicles.
So what does the market look like for heavy trucks? According to an April 2016 report by Stifel Financial Corp. (St. Louis, MO, US), the forecast will be down from 2015:
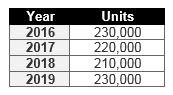
SOURCE: Stifel Financial Corp.
Meanwhile, Stifel reported that the medium duty truck segment, which is less volatile, was up in 2016.
An alternative source of market info, FTR (Bloomington, IN, US) announced an upturn earlier this month, with net orders for Class 8 trucks in North America projected to hit 19,300 units for November, a 41% increase over October. That still annualizes out to only 191,000 units, but FTR says inventories have finally dropped and manufacturing is regaining strength, connoting continued upward movement through early 2017. The table below shows Class 8 market share by manufacturer.
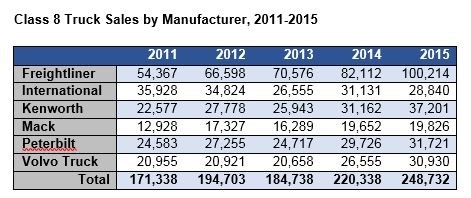
SOURCE: Ward’s Automotive Group, Motor Vehicle Facts and Figures 2015
http://cta.ornl.gov/vtmarketreport/heavy_trucks.shtml
Related Content
Cryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreSulapac introduces Sulapac Flow 1.7 to replace PLA, ABS and PP in FDM, FGF
Available as filament and granules for extrusion, new wood composite matches properties yet is compostable, eliminates microplastics and reduces carbon footprint.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fibers for composites
The structural properties of composite materials are derived primarily from the fiber reinforcement. Fiber types, their manufacture, their uses and the end-market applications in which they find most use are described.
Read MoreOne-piece, one-shot, 17-meter wing spar for high-rate aircraft manufacture
GKN Aerospace has spent the last five years developing materials strategies and resin transfer molding (RTM) for an aircraft trailing edge wing spar for the Airbus Wing of Tomorrow program.
Read MoreRead Next
CW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read More









.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)