Composites in the Martian suit
When humans do finally travel to Mars, they will have to be well protected from a less-than-hospitable environment. The suit designed to do the job is already in development at NASA, and it relies heavily on composites.
The race to send humans to Mars has begun. In late September 2016, Elon Musk announced that he and SpaceX (Hawthorne, CA, US) are working on plans to make human travel to Mars not just feasible, but (relatively) affordable. Musk thinks he can get the cost of travel to the Red Planet down to a meager US$200,000 per person, and he believes there could be millions of people living on Mars by 2060.
Competitor Boeing’s (Chicago, IL, US) CEO Dennis Muilenburg presented in early October his vision for an entire commercial space travel industry, replete with a variety of destinations in Earth orbit and new supersonic jets whisking travelers between continents in just a few hours. Capping it off, he asserted, “I’m convinced the first person to step foot on Mars will arrive there riding a Boeing rocket.”
Indeed, NASA is eager for its partners to help the space agency put people on Mars as soon as the 2030s. This effort will start in 2018 with a series of missions designed to test propulsion, spacecraft and, eventually, human performance at increasing distances from Earth, culminating in what NASA calls Earth Independence.
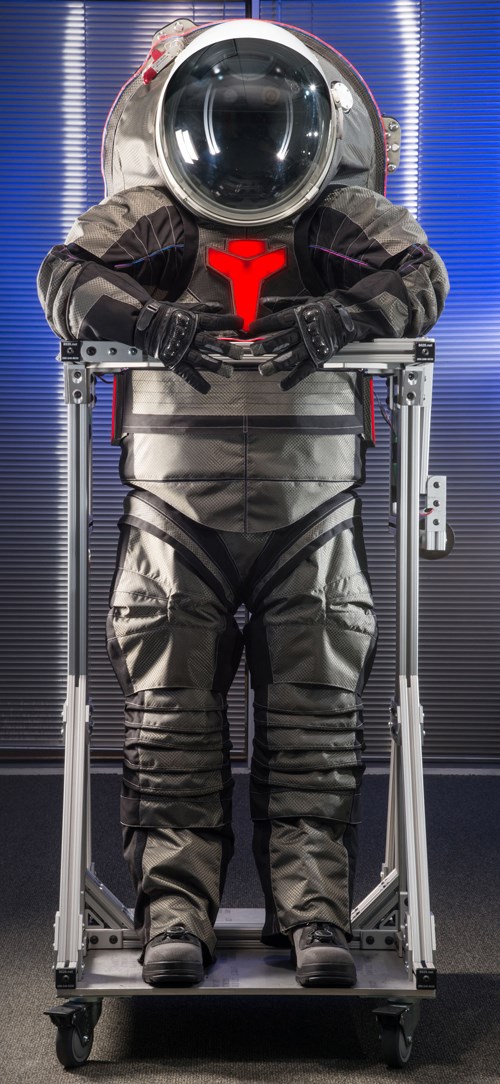

NASA’s Z-2 spacesuit prototype. One of the first spacesuit iterations designed specifically for use on the harsh Martian surface, NASA’s Z-2 features a hard upper torso (HUT), back hatch and briefs made with composites, primarily for impact and ballistics resistance. Although NASA provided general design principles for the parts, design engineering and prototype fabrication was performed by the University of Delaware – Center for Composite Materials — Applications & Technology Transfer Lab (UD/CCM/ATTL), which also fabricated a working prototype. Source: NASA
Whether humans first touch down on Mars in a SpaceX or Boeing vehicle, a top priority will be full and continuous protection to ensure their survival in a decidedly unfriendly Martian landscape. Setting aside for the moment concerns about deadly cosmic rays and gravity that is just 38% that of Earth’s, there are five Martian environmental factors that are immediately and particularly problematic.
The first is the atmosphere, which is 96% carbon dioxide. Compare this with Earth’s, at 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and other gases.
Second, the atmospheric pressure on the Martian surface averages 600 pascals, which is 0.6% of Earth’s mean sea level pressure of 101.3 kilopascals. This puts the Martian atmosphere below the Armstrong limit, meaning unprotected humans on Mars would suffer immediate and painful evaporation of their saliva, tears, skin mucous and whatever fluid exists in their lungs.
Third, on Mars, temperatures can range from a comfortable 70°F/21°C to an unlivable -225°F/-143°C. Fourth, there are dust storms of a size, ferocity and duration sufficient to cover whole regions of the planet’s surface.
Finally, there is the threat of falling micrometeorites. Because the Mars atmosphere is so thin, these impact the planet, for the most part, remain intact and, thus, present a very substantial ballistic hazard.
Anticipating these challenges, NASA has begun development of a new spacesuit. Called Z-2, it is designed for what NASA calls planetary extravehicular activity (EVA), that is, for astronauts who will climb in and out of vehicles and habitats as they travel and study the planet. Z-2 is a project of NASA’s Advanced Exploration Systems Division.
What a suit needs
The Z-series of suits feature a rear entry port that docks with the habitat or spaceship, allowing the astronaut to leave the suit and dirt outside. For Z-2, NASA decided on lightweight hard-shell components covering the torso to provide the astronaut better protection. Three composite parts make up the Z-2 torso: the HUT (hard upper torso), the brief, and an entry hatch that mounts to the back of the HUT. Each component must mate with bearings and seals, as well as the helmet and the arm and leg sections. Further, many of the life support and communication systems are mounted to the HUT and the hatch inside and outside the suit. The rigid composite torso could not sacrifice mobility and could impose only minimal weight increase.
To prove the viability of the Z-2 suit, NASA turned to ILC Dover (Frederica, DE, US), which has a long history of manufacturing spacesuits, going back to Apollo program days.
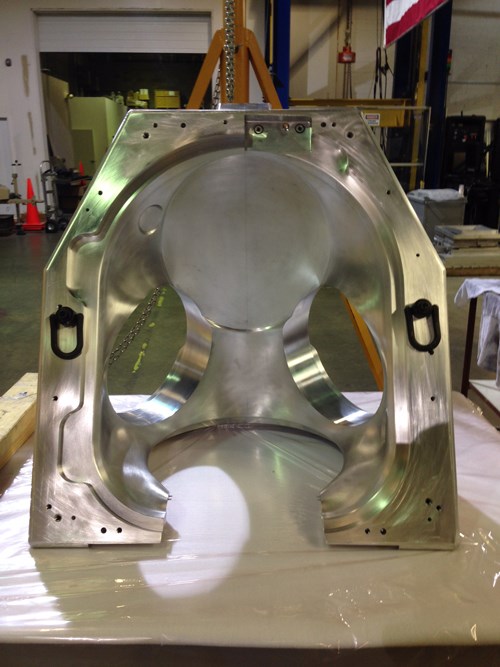
Toolmaking makes the difference. The aluminum female mold for the Z-2 HUT had to be separable to permit extraction of cured parts and avoid hang-ups. (The tool’s parting line is barely visible in the tool’s vertical center.) UD/CCM/ATTL did all of the tool design, simulation and process analysis for the Z-2. Source: UD/CCM/ATTL
Working as the prime contractor on the suit program, ILC Dover engaged the University of Delaware – Center for Composite Materials — Applications & Technology Transfer Lab (UD/CCM/ATTL) to help push spacesuit performance to the next level by optimizing design and manufacturing while reducing defects found in earlier composite parts.
This was a challenge, partly because NASA wanted a flight-quality test article that would be safe for human mobility trials and astronaut training in a vacuum chamber. “Project funding and timeline allowed for only one chance at fabricating the suit com- ponents, which was to be done under supervision of government quality auditors and required rigorous process documentation and control,” says Dan Molligan, assistant director for application development at UD/CCM/ATTL. Molligan notes that, “ATTL is an off-site ITAR restricted facility which has an infrastructure very unlike other universities; it has rigorous SOP, SMP, and quality standards which conforms to commercial industry protocol.”
Early in Z-2, ILC screened candidate materials (fiber and matrix) and processing methods. In addition to lightweight and high strength, materials had to be “space-qualified” and non-toxic. The team decided to base the reinforcement on high-modulus carbon fiber, adding outer layers of S-glass to improve impact resistance. Using woven fabrics (versus unidirectional) would further improve impact resistance. A tough- ened epoxy with good hot/wet performance and good processib- lity was selected as the matrix. Out-of-autoclave (OOA) processing of prepregs was selected to achieve near-autoclave performance at lower cost.

Managing the process. Z-2’s prime contractor, ILC Dover (Frederica, DE, US), wanted to fabricate the suit’s composite parts using an out-of-autoclave (OOA) process, but this proved unworkable. Instead, UD/CCM/ATTL employed PMTF-4A, a carbon fiber/epoxy prepreg from Patz Materials & Technologies (Benicia, CA, US), which made layup of the complex ply buildups and drop offs more practical. Source: UD/CCM/ATTL
Working from the functional requirements and feedback provided by ILC and NASA, ATTL engineers used solid modeling software to design the Z-2 component geometry. The HUT especially had highly contoured surface geometry. After ATTL completed the initial laminate design for the HUT, hatch door and brief based on structural analysis of static pressure and external load cases using FE software, CCM campus researchers ran impact simulations of various mission profile mishaps that could occur during planetary exploration, such as tripping and falling onto a rock.
While the impact study was going on, the team at ATTL designed molds for the HUT, brief and hatch. By then, the outer surfaces of the parts were fixed, and any design changes (i.e., thickness buildups, changes in laminate design) would affect only the inside surfaces, which would be controlled by a conformable vacuum bag. ATTL also conducted trials to develop a process for OOA prepreg by fabricating numerous test panels and subelements. During these trials, it became apparent that OOA processing would not produce Z-2 parts with acceptably low void content because debulking steps entrapped too much air in the prepreg. “Consequently, autoclave processing was chosen for final preform consolidation and curing, which required another round of process development, with the prepreg modified for autoclaving,” says Bill Patterson, techni- cal manager, at UD/CCM/ATTL. Ultimately, mechanical testing at ATTL showed no property loss from multiple debulks compared to panels consolidated and autoclaved in one step.
Geometry, geometry, geometry
The greatest challenge, say Molligan and Patterson, in designing and fabricating the Z-2 components was dealing with their geometric complexities. First, the interfaces between the torso components and between the torso and the helmet, arm sections and leg sections led to highly complex outer surfaces. Even for parts with uniform thickness, each preform layer consisted of many patterns due to the shear limits of the fabric feedstock material, each requiring precise location and shearing into the final shape.
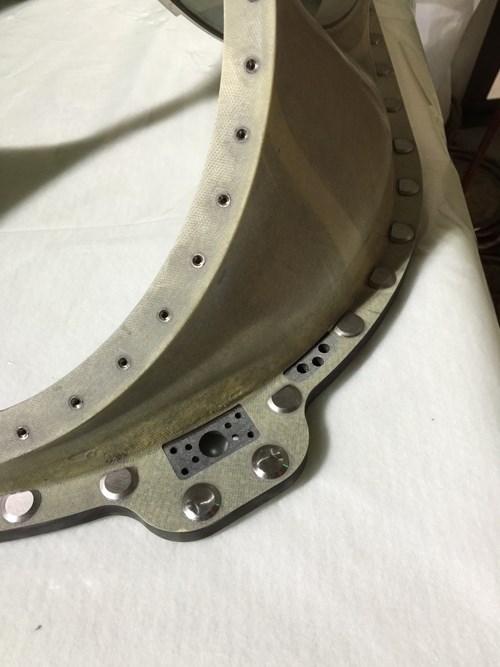

Performance key: Mating surface accuracy. Mating surfaces on the HUT and other Z-2 composite parts are critical because the suit must, first and foremost, maintain pressure at all times. UD/CCM/ATTL was challenged by the variable thicknesses of the composites, which required use of multiple ply drop-offs. These, when combined with the autoclave process, forced the use of several intermediate debulks to expel entrapped air. Source: UD/CCM/ATTL
Second, the parts were not of uniform thickness, but had local buildups at various hardware attachment locations. The main challenge was to make thick flanges in the HUT and the hatch to form the door-locking features that NASA used on previous HUTs. The locking mechanism consists of a toothed, linked belt that runs in a track in the inside surface of the HUT flange, and a string of gear teeth around the outer perimeter of the hatch. The belt is moved to engage and disengage the hatch teeth. On the hatch, the flange was roughly 1-inch wide by 2 inches high (25.7 mm by 50.1 mm) in cross-section.
For the hatch, NASA’s initial preference was to have composite teeth, as in the Mark III, for additional weight savings, but after numerous design iterations and process trials it was decided to provide a hybrid design where the outer perimeter with metallic teeth were retained to mitigate risk in the flight-quality test article. This would ensure that the load transfer from the hatch to HUT would be handled by a robust, fail-safe design.
Many options for forming the flanges were evaluated, but Molligan and Patterson chose to fabricate inserts from precured and machined prepreg after testing showed that there was no loss in interlaminar shear strength at the interface of prepreg and pre-cured insert. For the hatch, however, the only reliable way to ensure safety was to hybridize the component, using a metal outer ring and internal composite panel.
Finished prototypes were delivered to ILC Dover in July 2015. NASA conducted nondestructive testing of the parts, using flash infrared technology. ILC Dover subsequently assembled the composite parts with other suit components and delivered the finished Z-2 suit to NASA for evaluation.
Related Content
A new era for ceramic matrix composites
CMC is expanding, with new fiber production in Europe, faster processes and higher temperature materials enabling applications for industry, hypersonics and New Space.
Read MorePEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MoreCarbon fiber in pressure vessels for hydrogen
The emerging H2 economy drives tank development for aircraft, ships and gas transport.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Resin matrices for composites
The matrix binds the fiber reinforcement, gives the composite component its shape and determines its surface quality. A composite matrix may be a polymer, ceramic, metal or carbon. Here’s a guide to selection.
Read MoreRead Next
From the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More



















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)







