JEC Paris 2011 Review
This annual Paris trade event’s statistics signal an advanced composites resurgence.
When the numbers came in from the JEC Composites Show, they gave convincing support to the idea that in the realm of advanced composites, at least, the long recession is officially over. This year, JEC exhibitors covered a record surface area of 48,500m2 (522,000 ft2) at the Paris Expo (March 29-31). According to JEC’s show team, that is a 37 percent increase over the past six years. During the three-day event, JEC reportedly welcomed 1,122 exhibiting companies and 29,867 attendees (including exhibit personnel) from as many as 100 countries (vs. 27,500 in 2010), with 70 percent from outside France.
Given this kind of growth, it was no surprise that JEC’s second annual International Composites Summit (I.C.S.), which ran parallel to the show and included 100 papers form presenters hailing from 15 countries, was declared a great success. Attendance topped 2,000, with delegates arriving from all over Europe, including the Russian Federation. JEC reports that figure was 25 percent greater than last year’s I.C.S. The focus of 2011 was on Automotive and the Global, with emphasis on industrial-grade carbon fiber suitable for automotive composites in a mass-production environment. As noted in the May issue, the JEC show floor reflected the automotive/carbon fiber emphasis, with many applications of carbon in evidence on a number of new supercars and concept vehicles, including BMW’s forthcoming all-electric commuter car, the i3. (See “JEC Paris highlights" under Editor's Picks" at top right.)
On the show floor
The HPC staff was on hand and, as always, on the lookout for those new product introductions and other noteworthy developments of interest to HPC readers. The following capsulize staff observations not included in the “JEC Paris highlights” report in the HPC May 2011 issue.
Low-thermal-mass tooling
Advanced Composites Group Ltd. (ACG, Heanor, Derbyshire, U.K.) was in the spotlight for Carbovar composite tooling technology, the winner of the JEC Innovation Award in the Equipment category. Developed jointly with Integran Technologies (Toronto, Ontario, Canada), the technology combines ACG’s lightweight carbon prepregs and Integran’s Nanovate-NV nickel-iron alloy surface coating. Carbovar reportedly has all the advantages of a composite tool, such as low thermal mass, light weight and lower cost, with the surface durability and hardness of a metal tool. The two companies continue to optimize the tool substrate and coating to minimize thermally induced distortions and are looking for interested industry evaluators.
Bagging materials & durable composite tools
Airtech International Inc. (Huntington Beach, Calif.) provided live demos of custom-engineered vacuum bagging materials for infusion as well as solutions for hollow stiffeners. Many new products were on display, including additions to the company’s extensive tooling range. Beta Prepreg, a JEC Innovation Award finalist in the Equipment category, is a tooling prepreg with a unique toughening technology. Based on a benzoxazine resin system developed by partner Henkel AG & Co. (Düsseldorf, Germany), it reportedly can be stored at room temperature for up to six months with no loss of tack. Properties are superior to conventional epoxy and bismaleimide (BMI) systems, says the company, with high glass-transition temperature and high-temperature service stability for long tool life. Also on display: new super-wide bagging film, up to 12m/39 ft wide, for reducing layup time when fabricating vacuum bags for big parts, such as wind blades; and TB G48, a new cost-effective, high-temperature carbon fiber tooling board for mold support, jigs and fixtures.
Laser projection with debris sensor
Assembly Guidance Systems Inc. (Chelmsford, Mass.) demonstrated its new ProjectorVision laser projection system. The system is designed to prevent foreign object debris (FOD) from ruining a part. The machine vision system automatically detects any debris or stray materials in the mold during the laser-guided layup process and then locks the system to prevent further progress until the debris is removed.
Resin-infused demonstrator
Cytec Engineered Materials (Tempe, Ariz.) held a press conference at its stand to describe how the company leverages applications research and engineering to achieve breakthroughs in composite material applications. Rob Blackburn, Application Research and Engineering Team leader for Europe described a demonstrator forward fuselage of a business jet, which showed the feasibility of resin infusion when coupled with process improvements such as use of a barrier film to protect the honeycomb core from resin ingress. He also discussed work on infusion of the rear pressure bulkhead, for an unnamed major commercial jet, based on Cytec’s PRIFORM resin-infusion materials. According to Blackburn, the market is demanding advancements in composites, and “the requirements lead, while applications follow.”
Epoxy toughening agents
Dow Chemical Co. (Midland, Mich.) offered two new product lines at the show. New FORTEGRA epoxy toughening agents come in three types. The 100-Series is based on proprietary Dow block copolymer technology. It increases epoxy’s ductility yet maintains low viscosity. The 200-Series consists of elastomer-modified functional adducts that improve fracture toughness and peel strength. The 300-Series includes stable dispersions of preformed, novel core shell rubber particles in epoxy, which have minimal impact on thermomechanical composite properties. New VORAFORCE products include epoxy resin systems for composites fabricators. The epoxy-based systems reportedly deliver exceptional thermomechanical properties and are compatible with carbon fiber.
Multiaxial reinforcement converting
Sporting a new logo and enhanced Web site, Formax (Narborough, Leicester, U.K.) announced a 20 percent sales increase in 2010 that has enabled further investments in its multiaxial technology. Specifically, the company has purchased and installed a new Mali-tronic carbon multiaxial machine from Karl Mayer Textilmaschinenfabrik GmbH (Obertshuasen, Germany), which will enable production of unique new biaxial fabric constructions in variable widths to meet customer specifications. A new laminating line is forthcoming, which will combine surface veils with existing fabrics for Class A surfaces.
Laser-guided kitting system
Gerber Technology (Tolland, Conn.) announced LaserKit, a new laser-guided kitting tool, from its Virtek Vision International business unit. The new product helps workers assemble accurate kits for composite layup. It does so by indicating the correct sequence of plies to be picked from the cutting table, in addition to minimizing material waste by calculating more efficient nesting. Field tests reveal that LaserKit enables users to reduce composite cutting and kitting times by as much as 40 percent while decreasing the possibility of operator error. Available as an option to LaserKit is a lightweight printing device worn on a worker’s belt strap that prints labels automatically or on demand, significantly accelerating the ply identification process. Labels can be affixed to individual plies or completed kits. In fact, says the company, multiple kits can be nested together, cut and then picked from the same table.
Pilot line for carbon fiber research
Harper International (Lancaster, N.Y.) had its new corporate logo on display and emphasized its recent contract award for a full pilot-scale carbon fiber processing line, valued at more than $12 million (USD). A custom-designed conversion process, the carbon fiber line will support Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s (ORNL) research center for its collaborative Low Cost Carbon Fiber research and development effort. Harper is ORNL’s technical and implementation partner for engineering, process equipment, installation and startup of the line, which will enable ORNL to process multiple precursor platforms, including low-cost lignin. Also announced was the company’s “next generation” of custom oxidation ovens that incorporate several process improvements, including proprietary and unique atmospheric seals that reduce fugitive emissions, increase the active volume of the oven and offer reduced energy consumption.
Polyimide aerospace composites
IST Corp. (Industrial Summit Technology, Tokyo, Japan and Parlin N.J.) together with its Tokyo-based subsidiary Super Resin Inc., featured its development of advanced precision composites using its high-temperature polyimide resins for the aerospace industry. SKYBOND 800 FRP is a novel, high-temperature polyimide composite made in a proprietary two-stage resin-cure system, with a very low void content, making it ideal for use in high-temperature primary structure, says the company.
Marker-making technology
Cutting table manufacturer Lectra (Paris, France) released the newest version of Diamino, its marker-making solution. DiaminoTechTex (for automotive, composites and industrial fabrics) is designed to maximize marker-making for all pieces. It optimizes material consumption at the development and production stages using two different methods, depending on the material to be cut and the complexity of the model. Interactive marker-making is based on a manual method, and automated marker-making is managed entirely by Diamino and its algorithms. The software also offers a new rapid optimization function for existing markers, enabling manufacturers to save an average of 1 percent in material. The Optimizer function can be used on markers created interactively and on markers created in automatic mode.
Vacuum holding fixture
First-time exhibitor Micado CAD-Solutions (Lienz, Austria) impressed showgoers with its unusual Octopus vacuum holding fixture for aerospace applications. The company, which specializes in complex design solutions for the aerospace, automotive and sporting-goods markets, says the CATIA-designed fixture weighs less and is up to 40 percent less costly than more traditional fixturing devices, thanks to off-the-shelf tubing combined with a computer-controlled vacuum system.
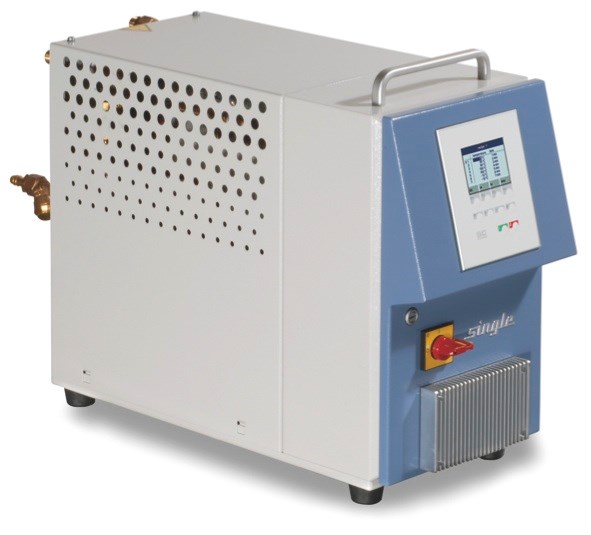
Mold-temperature control systems
SINGLE Temperiertechnik GmbH (Hochdorf, Germany) displayed hot-water mold-temperature control systems for temperatures up to 225°C/437°F. SINGLE notes that temperature control of molds with heat transfer media is a method that has been used for many years by plastics processors and can provide similar benefits for composites processors. “Even the high processing temperatures required by the composite industry do not eliminate the use of water as a heat-transfer medium. Water provides a significantly higher heat-transfer capacity thanks to its heat-conduction and heat-transfer properties, which are superior to those of oil,” said Karlheinz Gruber, managing director of SINGLE. At the show, the company emphasized a new compact hot-water temperature control system that has a heating capacity of 6 kW and a flow rate of up to 30L/min (7.9 gal/min) for temperatures as high as 225°C/437°F.
Related Content
JEC World 2022, Part 1: Highlights in sustainable, digital, industrialized composites
JEC World 2022 offered numerous new developments in composites materials, processes and applications, according to CW senior editor, Ginger Gardiner, most targeting improved sustainability for wider applications.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Resin matrices for composites
The matrix binds the fiber reinforcement, gives the composite component its shape and determines its surface quality. A composite matrix may be a polymer, ceramic, metal or carbon. Here’s a guide to selection.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Composites fibers and resins
Compared to legacy materials like steel, aluminum, iron and titanium, composites are still coming of age, and only just now are being better understood by design and manufacturing engineers. However, composites’ physical properties — combined with unbeatable light weight — make them undeniably attractive.
Read MoreRead Next
JEC Paris 2011 highlights
The news from this annual Parisian in-gathering of composites professionals is heavily weighted toward automotive lightweighting.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More


















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)












