COMPOSITES+POLYCON 2009 Showcase
Despite the deepening recession, composites pros returned to the show in its new time slot to explore the wealth of products and services collected here.
The American Composites Manufacturers Assn.’s (ACMA, Arlington, Va.) COMPOSITES+POLYCON trade show took its first turn in its new winter time frame, Jan. 15-17, in Tampa, Fla. It was the show’s first outing since a 2008 hiatus that resulted from ACMA’s decision to vacate its show’s traditional fall time slot. For several years, the ACMA and Professional BoatBuilder’s IBEX shows had been held within the same 30-day period, so the move was intended to spare marine-oriented exhibitors and visitors the inconvenience of back-to-back exhibitions. The timing of the show was unfortunate, however, coming so soon on the heels of the late 2008 revelations about the global credit crisis, and as a result, attendance was down compared to figures reported in recent years. Indeed, some of the 180 exhibitors and ~2,600 attendees wondered aloud how soon the economic downturn might end and how, in the meantime, the composites industry would fare. But the general sentiment of those present was “soon” and “well,” respectively.
Evidence in the exhibit hall suggested that the poor economy has many composites professionals thinking outside the box and looking intently at new applications and markets. Several CT readers encountered in the aisles indicated that exploration of applications in what many speculated would be recession-resistant markets — renewable energy, particularly wind energy, and ballistic protection — might help some processors and suppliers see themselves through the downturn. Additionally, the array of products and technology on display demonstrated that even though the economy is on idle, the composites industry is not one to sit idly by.
Appropriately, the event keynote, given by Roger Tutterow of Mercer University (Macon, Ga.), examined the roots of the current economic crisis and offered statistics in support of various economic indicators. His conclusions: It may look bad now, but cautious optimism is in order because the credit crunch, in his opinion, will start to ease in the second quarter of this year. Although housing starts are way down, particularly in coastal Florida, California, Las Vegas and along the East Coast, he pointed out that other markets “aren’t so bad,” noting that the remodeling market will provide some opportunities. He also believes that infrastructure projects will grow, providing some momentum, and that bond market trends show signs of recovery. Tutterow told attendees to look for signs of recovery in the stock market first, followed a few months later by the overall economy — with the latter coming in late 2009 or early 2010.
Educational opportunities
At COMPOSITES+POLYCON 2009, several papers and presentations focused on life cycle analysis (LCA), a substantially complex process of quantifying, via the 14040 ISO standard on environmental management, a part’s total impact on the environment. According to Michael Lepech of Stanford University (Palo Alto, Calif.), LCA takes into account everything that goes into a product (power needs, raw materials, etc.) and everything that comes out (solid waste, emissions, etc.), enabling engineers to identify often unexpected energy-consumption “hot spots.” In one example, students conducted and compared LCAs of a large composite fish tank for an aquarium and a concrete version. Somewhat surprisingly, the concrete tank, despite its much lower cost, created more environmental issues because of the greater energy and transport costs incurred when working with concrete. Ashland Performance Materials (Dublin, Ohio) contributed resources for the Stanford LCA study.An array of other technical papers was available, including an examination of CompForm, a reportedly ultrafast automated method for preforming multiaxial fabrics using light-curable binder. Offered by American GFM Corp. (Chesapeake, Va.), the method has been implemented successfully for structural automotive components. Other highlights included a description of an all-composite residence successfully constructed by Kreysler & Assoc. (American Canyon, Calif.) and a report on the current status of a melt-spun, high-modulus polypropylene fiber produced by Greer, S.C.-based Innegrity LLC (see Innegrity's "Product Showcase" item below).
ACE awards highlights
Awards for Composites Excellence (ACE) nominees were impressive. They ran the gamut from composite utility poles and rapid preforming technologies to a pultrusion process that incorporates structural core material, and uniquely flexible composites. Among the standouts was Ershigs’ (Bellingham, Wash.) entry, a mast system developed for NASA to provide lightning strike protection. It involves poles 104 ft/31.7m tall and 7 ft/2.1m in diameter, with a multi-inch-thick laminate in each that weighs more than 50,000 lb (22 metric tonnes). The Best of Show award went to Berry Plastics Corp. (Franklin, Mass.), reportedly the world’s largest manufacturer of duct tape, for its hand-applicable peel-and-stick building wall-blast reinforcement system, which comprises a ±45° aramid fiber scrim in an extruded polyurethane matrix.By show’s end, ACMA had announced yet another departure from its previous bicoastal regimen. Next year, the show won’t return to the West Coast after its stop this year in Miami. Instead, COMPOSITES+POLYCON 2010 will head for Las Vegas, Nev., opening Feb. 9 at the Mandalay Bay Resort and Casino.
C+P 2009 Showcase
CT editorial staffers were on hand for the show, and — for the benefit of those not able to be at the Miami event — collected the following sampling of the technologies and services spotlighted by exhibiting suppliers, listed below in alphabetical order. To pursue more information about these companies or their products and services, click on the links provided under "Related Suppliers," at right.
New name, doubled capacity
Ahlstrom Glass Nonwovens LLC (formerly Ahlstrom Specialty Reinforcements LLC, Bishopville, S.C.) reinforced the company’s recent name change, which was made to better reflect the diverse fiberglass products manufactured by the company and now offered to the North American marketplace. Products include multiaxial knits, woven roving, chopped strand mat and fiberglass veil. The company also announced that it is doubling its manufacturing capacity and adding multiaxial and stitch bonding equipment at the Bishopville site.
Initiators & curing agents
Akzo Nobel Polymer Chemicals LLC (Chicago, Ill.), a provider of a wide range of organic peroxides, highlighted its strong technical support to customers who purchase its trademarked Trigonox, Perkadox and Cadox initiators and curing agents. The company also recently announced the availability of Perkalite, a synthetic, layered, double-hydroxide nanoscale organoclay material that is suitable as a flame retardant synergist in plastics and composites that must comply with flame retardant regulations.
Cultured marble casting resinAOC LLC (Collierville, Tenn.) spotlighted Vicast A830, a casting resin for cultured marble applications, designed to accommodate more filler and, therefore, displace 10 to 20 percent more resin, allowing the user to reduce material costs. Engineered for use with marble-quality calcium carbonate or specific lightweight fillers, the nonthixotropic, low-shrink resins incorporate dicyclopentodiene (DCPD) chemistry. They are prepromoted for room-temperature cure using methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) initiator.
Polyester resin additivesArkema Inc. (Philadelphia, Pa.) exhibited its chemical additives for improving composite processes and allowing fabricators greater control of unsaturated polyester resin cure. Featured was its trademarked BlocBuilder RC 50 resin additive, a controller and initiator combined into one compound, targeted to compression molding processes that use SMC and BMC as well as pultrusion processes with cure times above 140°F/60°C. The compound reportedly extends pot-life stability for increased storage and shipping times, reduces scrap material and cleanup time, and improves consistency and quality, says the company. Bob Dixon, market manager, explained that this reactivity controller affects the rate of cure and stability of unsaturated polyester combined with organic peroxides during gelation and through final cure. “Composite fabricators want a slower rate of resin reaction before molding, while still maintaining similar cure conditions, and a faster rate at the elevated in-press temperatures to increase production efficiency. BlocBuilder RC 50 prevents premature gelling and is very effective in closed molding applications.” Environmental and sustainability benefits include the potential to transport it without the need for refrigerated trucks and less waste associated with premature gelling. From a processing standpoint, line speeds and compression time can be improved, resulting in greater throughput and lower cost per part.
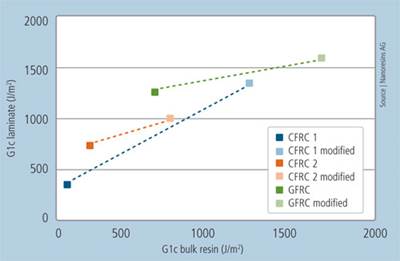
Cure monitoring, life cycle analysis, pultrusion bio-resinAshland Performance Materials (Dublin, Ohio) featured the SmartTrac technology at its booth, a technology recently acquired from Signature Control Systems Inc. (Denver, Colo.). SmartTrac impedance monitoring probes, placed within a tool, determine the exact moment of cure in a thermoset resin system, which helps improve cycle time and reduce scrap.
The company also played an integral part
in the publication of several sustainability and life cycle analysis
(LCA) papers presented at the show conference, contributing resources
for LCA studies performed at Stanford University, which showed that
composites can have positive environmental impacts.
Polyurethane cure control, EPA-approved carbon nanotubesBecause polyurethane cures quickly, there is a small window of time for part sprayup/layup before the onset of cure. Historically, this has restricted part size. With this challenge in mind, Bayer MaterialScience LLC (Pittsburgh, Pa.) spent the last several years working with personal watercraft (PWC) supplier Camoplast Inc. (Roxton Falls, Quebec, Canada) to develop a new urethane formulated to delay cure and widen the process window during manufacture of a PWC boat hull using long-fiber injection (LFI) technology (see photo #3, at right). New Baydur STR 814 polyurethane allows time enough for four automated Krauss-Maffei (Munich, Germany) spray heads to deliver material into the 12-ft/3.6m long, 3-ft/0.9m wide hull in a nickel-shell female tool prior to mold closure and cure initiation. The Krauss-Maffei long-fiber system increases glass output from 180 g/sec to 300 g/sec. The new boat requires only four molds and is 25 percent lighter than previous versions that comprised 60 parts, each individually compression molded from polyester sheet molding compound. A new gel coat that provides its Class A surface is provided by Sogel (Longueuil, Quebec, Canada) and was designed specifically for use with polyurethane (see Sogel item below).
Bayer also announced that its Baytubes multiwalled carbon nanotubes have received regulatory approval from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This allows Bayer to sell the nanotubes in the U.S. Bayer is targeting thermosets and thermoplastics for the material, mainly in aircraft, transportation, sporting goods and building and construction applications. Reported benefits of the Baytubes include improved mechanical strength and antistatic properties. Diameters range from 5 nm to 20 nm, in lengths from 1 to >10 microns. The nanotubes, says Bayer, are recommended for use with letdown ratios of 0.5 to 1.5 percent (by weight) in thermosets and 3 to 5 percent in thermoplastics. Currently, Baytubes are made in Germany at an annual rate of 60 metric tonnes (132,280 lb), but additional capacity of 200 metric tonnes (444,925 lb) is expected to come online later this year.
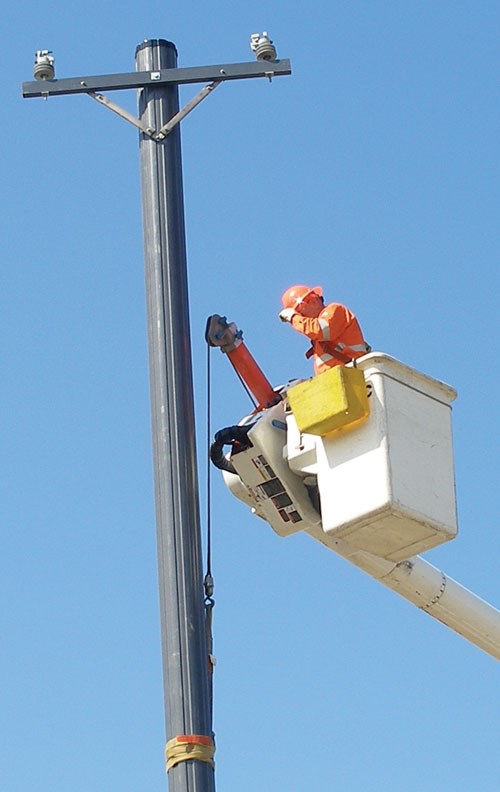
Pultruded utility polesPultrusion specialist Bedford Reinforced Plastics (Bedford, Pa.) featured in its booth a utility pole that it manufactures for customer Duratel (Chicago, Ill.). In development for several years and introduced to the market in early 2008, the poles were pultruded with E-glass provided by Owens Corning (Columbus, Ohio) and polyester resin from Ashland (Dublin, Ohio). The charcoal gray poles range in length from 35 ft to 55 ft (10.7m to 16.7m) and weigh about two-thirds less than traditional wood poles (300 lb/136 kg vs. 1,000 lb/220 kg for a 40-ft/12m pole). Bedford employs a UV additive in the resin and a UV matting on the surface of the pole, which are nonconductive and accept existing hardware used on wood poles. Other features include a 80-year life span (vs. 25 to 30 years for wood), no corrosive or toxic additives, tree conservation and recyclability at end of use. Duratel says it is in the process of installing its poles in several metropolitan locations as a demonstration of their capability and suitability.
Closed molding education
Composites One (Arlington Heights, Ill.) emphasized its participation in the Closed Mold Alliance, an industry group that also includes Magnum Venus Plastech (MVP, Clearwater, Fla.), RTM North (Vonastra, Ontario, Canada) and FormaShape (Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada, a div. of WhiteWater Composites Ltd.). The Alliance aims to offer composites manufacturers closed mold education, expert consultation, tooling assistance and start-up training. Closed Mold University is the group’s series of educational programs offered at locations across the U.S. and Canada over the next several months.
Process control collaboration
CompuDAS (Shelton, Wash.), shared booth space with collaborator Wisconsin Oven (East Troy, Wis., see item below), to demonstrate its expertise in data acquisition, process control and turnkey systems for controlling and documenting autoclave, press and oven processes, noting that more than 500 CompuDAS systems are in place worldwide.
Gel coat & barrier coat alternativesCCP - Cook Composites & Polymers (Kansas City, Mo.) featured several new products at its booth, including IMEDGE Polymer Coating Technology (PCT), a new alternative to traditional gel coats and barrier coats. The in-mold coating sprays on like gel coat and is MACT-compliant but reportedly delivers superior blister and crack resistance and is extremely resistant to weathering and fading. Also on display was new NuTack-BLU, a reactive tackifier spray for infusion processing that chemically reacts with the infusion resin for better interlaminar adhesion of reinforcement plies.
Cutting system softwareEastman Machine Co. (Buffalo, N.Y.), a manufacturer of fabric cutting systems, demonstrated its cutPRO software. During the show, the software operated a cutting machine in the exhibit booth, cutting a glass fiber fabric. The company reported that it has been very active in developing cutting and nesting software and reportedly has placed several machines into the wind turbine blade manufacturing market.
Polyisocyanurate & polyurethane foamElliott Co. of Indianapolis Inc. (Indianapolis, Ind.) reported that its rigid polyisocyanurate and polyurethane foam products are specified worldwide in diverse applications, including coolers and freezers, architectural panels, chemical storage tanks, truck and trailer bodies, boats, pipe insulation and more. The company emphasized that its polyisocyanurate (or polyiso) foam panel sheets have improved physical performance properties and greater dimensional stability over a wider temperature range than its original polyurethane-based products.
Epoxy hardener chemistryEvonik Degussa Corp. (Parsippany, N.J.) distributed information on its specialty crosslinker chemicals, formulated specifically for wind turbine blade manufacturers. Its isophorone diamine VESTAMIN IPD, one component of the hardener used to cure epoxy resins, imparts good mechanical properties, higher stiffness and better thermal stability when added to epoxies for wind blades, claims the company.
Cast polymer productsGruber Systems Inc. (Valencia, Calif.) reported high visitor traffic at its booth, which featured new products for the cast polymer industry. President and CEO John Hoskinson spotlighted a new vanity bowl mold, termed the Winston Oval Floating Bowl, which gives cultured marble manufacturers an innovative and distinctive contemporary product option. Also on display were Gruber’s latest Granatex granite-effect fillers for solid surface and cast polymer manufacturing applications. The company also offers a full line of Seamless-brand adhesives and accessories.
Nonhalogenated flame retardantHuber Engineered Materials (Atlanta, Ga.), citing increased sensitivity to emerging regulations that restrict the use of halogen-based fire retardants in composite and plastic products, introduced its MoldX line of optimized alumina trihydrate (ATH) flame retardant. Designed to comply with European mandates against the use of halogenated retardants, MoldX has been modified by Huber to provide high loadings and low viscosity. High viscosity has historically been a challenge of high ATH loadings, Huber says, and the chemistry of MoldX is formulated to address those challenges. The company reports that the ATH thermally decomposes to water and offers a slow-burn profile with less smoke. Huber notes that, historically, regulations were more concerned with flame spread, but now the emphasis is tighter restrictions on smoke toxicity — thus halogens are the target. ATH is recommended for thermosets, including styrenated polyesters, polyurethanes and epoxies, and it is now suitable for use in sheet molding compound (SMC) and bulk molding compound (BMC) applications. Huber cautions users to take greater care when using ATH in thermoplastics (compared to thermosets) because mechanical properties can be more easily affected. Use with high-temperature thermoplastics is not recommended because ATH decomposes at 230°C/446°F.
Also available are a 16-position Type J thermocouple jack panel, transducers and solenoids. Temperature uniformity is +3.9°F/-6.8°F at 350°F (+2.2°C/-13.8°C at 176.7°C).
The company also touted its recently announced “E-Pack” oven upgrade program, which includes thicker wall panels, higher efficiency motors and other energy-saving items that result in considerable cost savings if an oven is operated more than 2,000 hours per year.
Related Content
PEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: Airbus A400M cargo door
The inaugural CW From the Archives revisits Sara Black’s 2007 story on out-of-autoclave infusion used to fabricate the massive composite upper cargo door for the Airbus A400M military airlifter.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Composites fibers and resins
Compared to legacy materials like steel, aluminum, iron and titanium, composites are still coming of age, and only just now are being better understood by design and manufacturing engineers. However, composites’ physical properties — combined with unbeatable light weight — make them undeniably attractive.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Tooling for composites
Composite parts are formed in molds, also known as tools. Tools can be made from virtually any material. The material type, shape and complexity depend upon the part and length of production run. Here's a short summary of the issues involved in electing and making tools.
Read MoreRead Next
Resin systems update: The greening of thermosets
Thermoset resin formulators seek environmental benefits as customers demand reduced cost and increased performance.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More










.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)